Cone Dystrophy
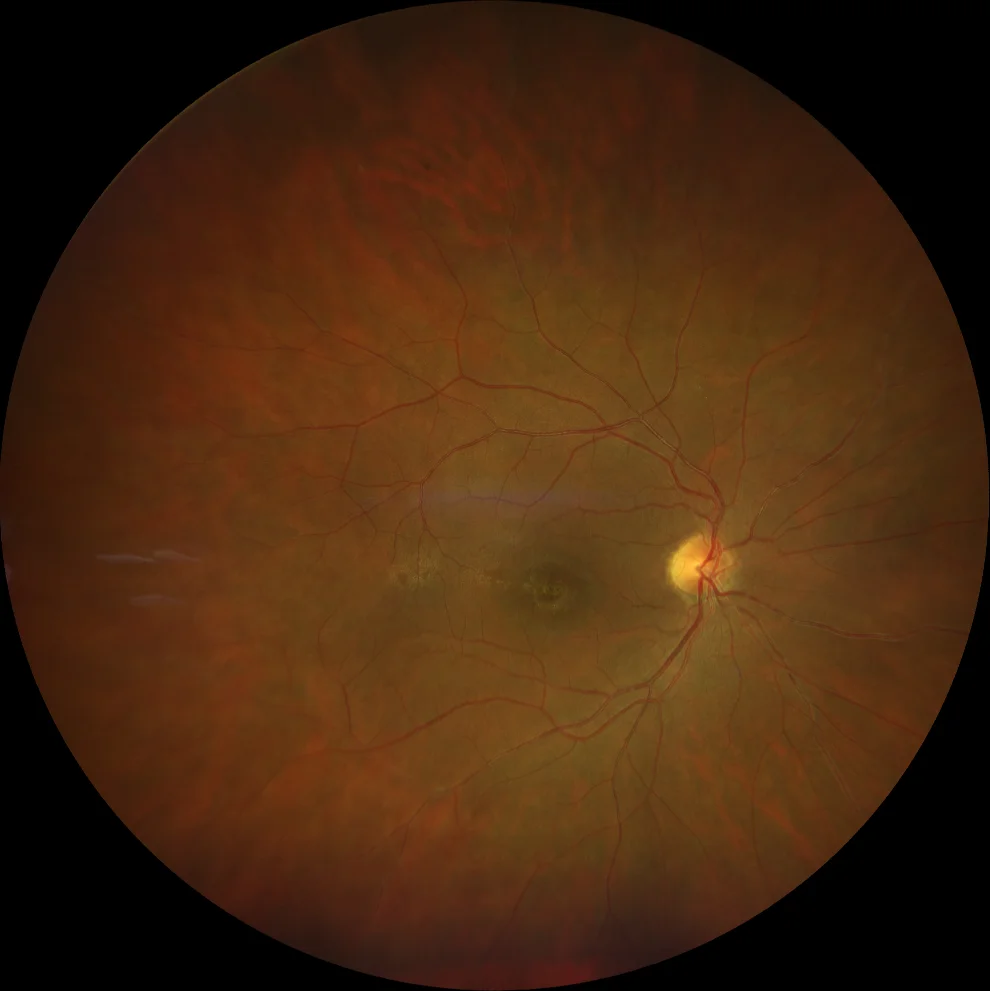
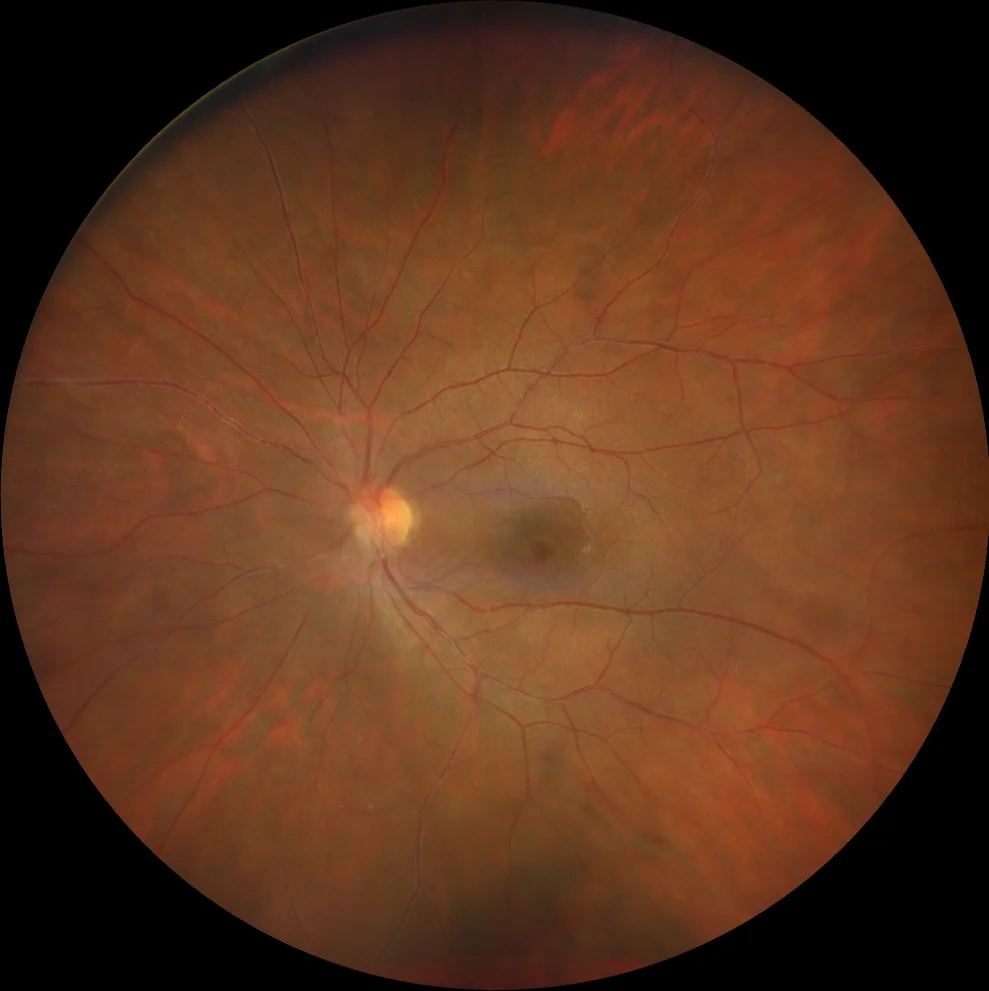
Cone dystrophy. A and B. Color fundusography (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the right and left eyes, showing bull's-eye pigmentary changes, more pronounced in the right eye.
Cone dystrophy. A and B. Color fundusography (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the right and left eyes, showing bull's-eye pigmentary changes, more pronounced in the right eye.
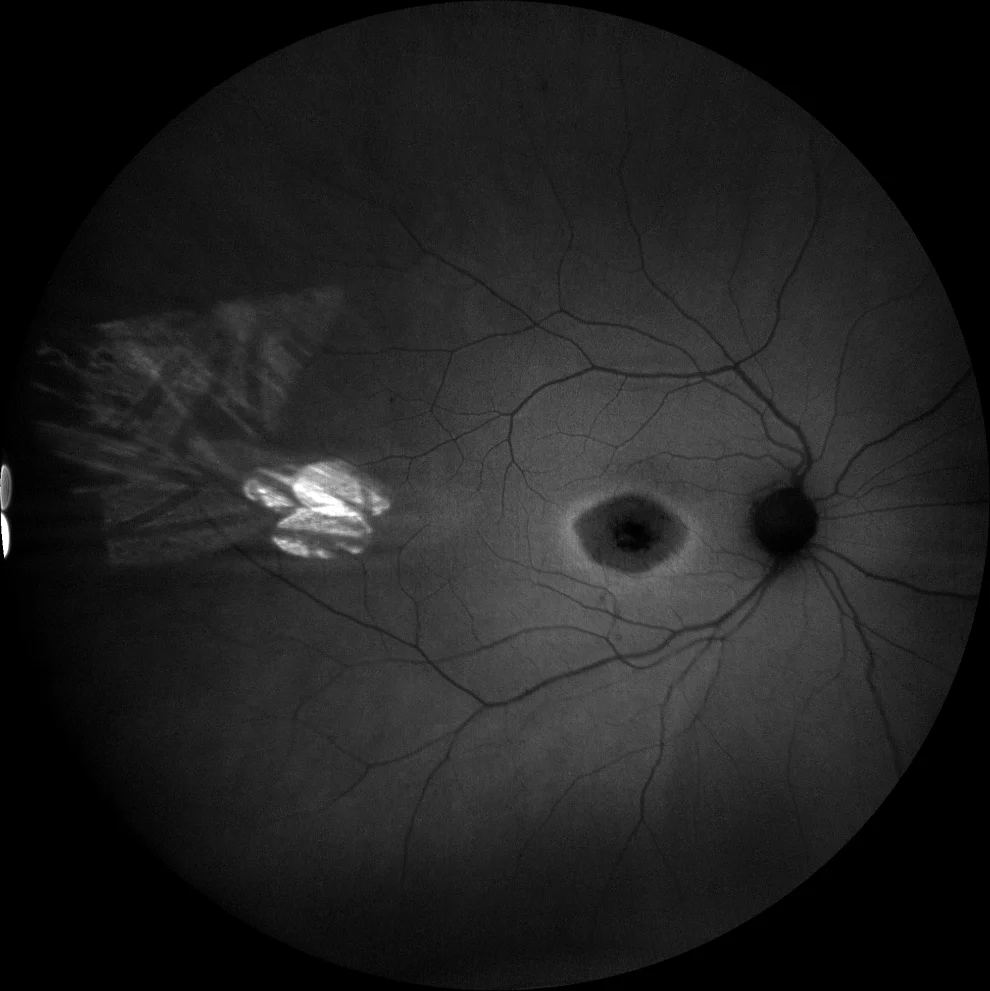
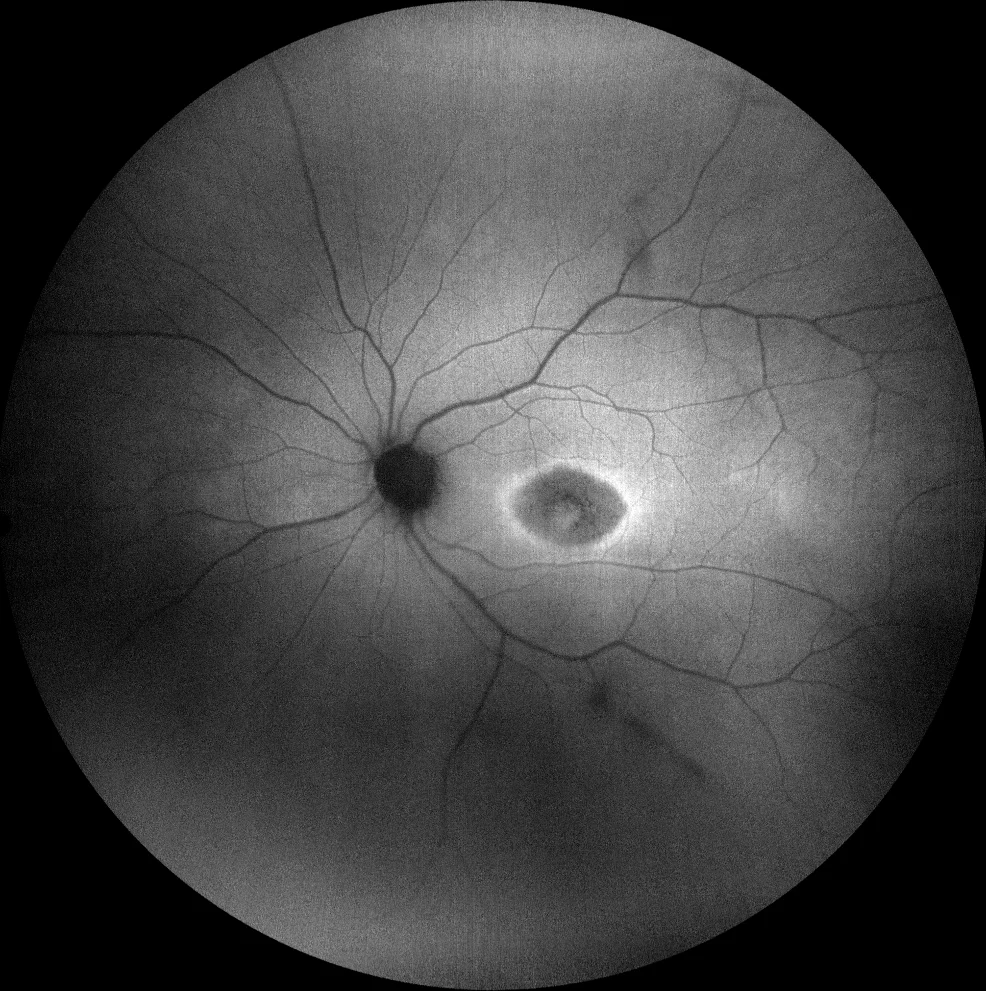
C and D. Autofluorescence images (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the right and left eyes, showing retinal hypoautofluorescence in the bull's eye area, surrounded by a bilaterally symmetric hyperautofluorescent halo.
C and D. Autofluorescence images (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the right and left eyes, showing retinal hypoautofluorescence in the bull's eye area, surrounded by a bilaterally symmetric hyperautofluorescent halo.
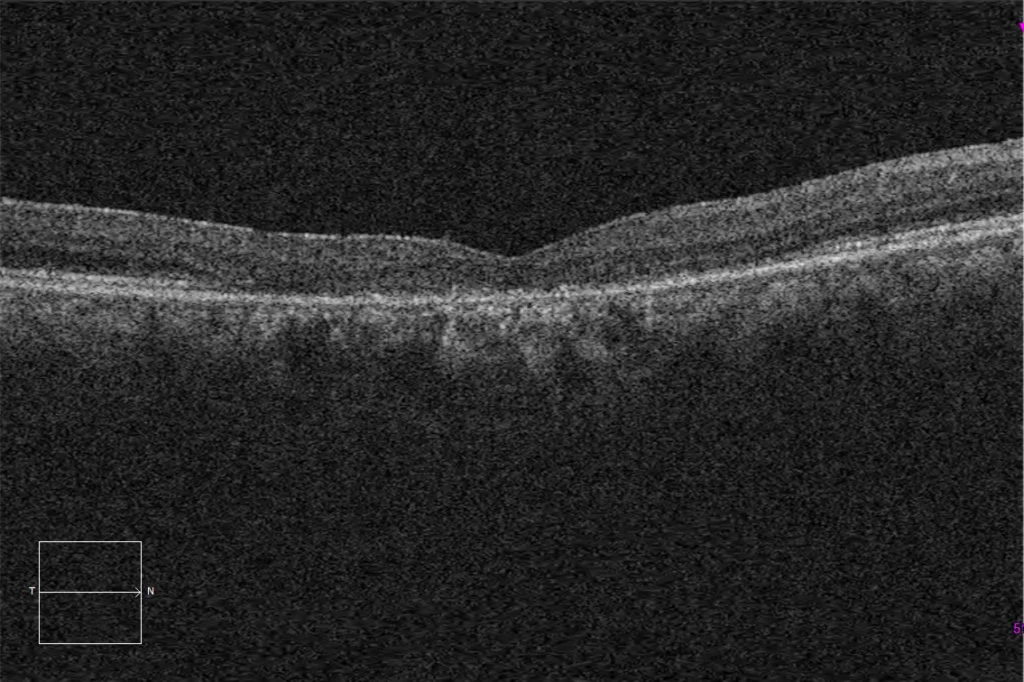
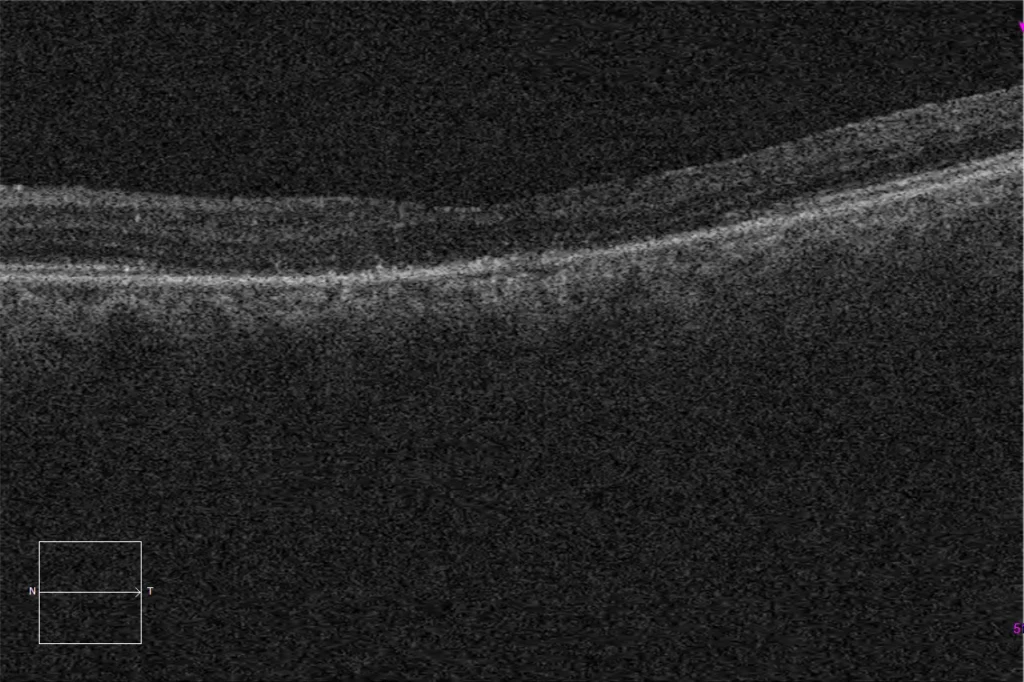
E and F. Macular HD optical coherence tomography (Cirrus 5000, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the right and left eyes, showing loss of the ellipsoid and subfoveal external limiting layers, corresponding to the lesion observed in the autofluorescence images.
Description
Cone dystrophies represent a heterogeneous group with more than 25 identified causative genes.
The onset of symptoms usually occurs from adolescence, including decreased central visual acuity, dyschromatopsia, hemeralopia, and photophobia. The disease tends to progress over the years.
Initially, the fundus may not show alterations, later acquiring the appearance of symmetrical bull’s eye atrophy or more extensive macular atrophic plaques. Atrophy in the optic disc may also be found. Optical coherence tomography may show a decrease in thickness of the outer layers. The definitive diagnosis is made with electroretinogram, which usually shows marked photopic dysfunction, which may be accompanied by scotopic dysfunction in more advanced stages of the disease.
There is currently no treatment for this group of pathologies. Follow-up is required to detect possible complications, as well as counseling regarding potential low vision aids or adaptations in daily life.