Hereditary Retinal Dystrophies
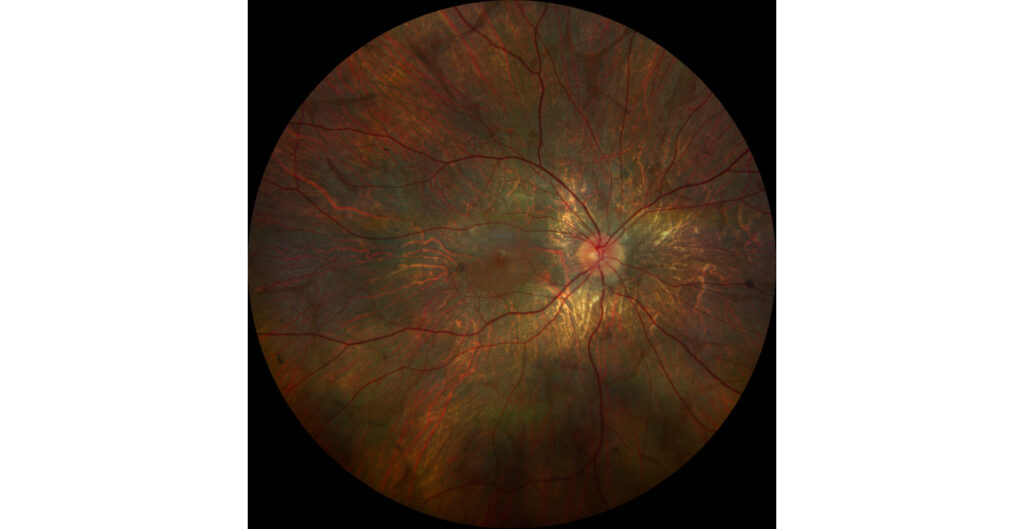
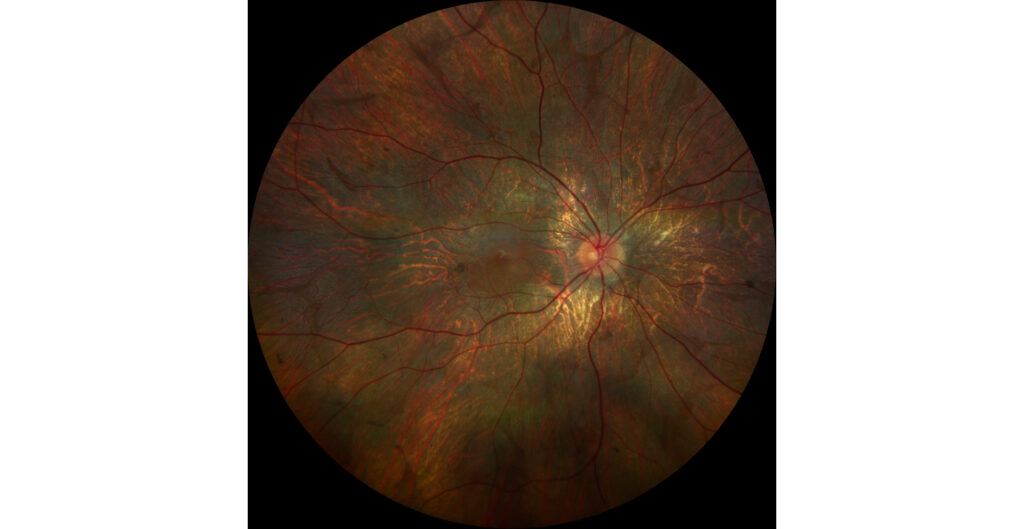
Retinography (Clarus 700, Zeiss): retinal atrophy and diffuse RPE with pigment deposition. There is a central island of healthy retina, as well as several areas of healthy retina scattered around the periphery (A1, A2).
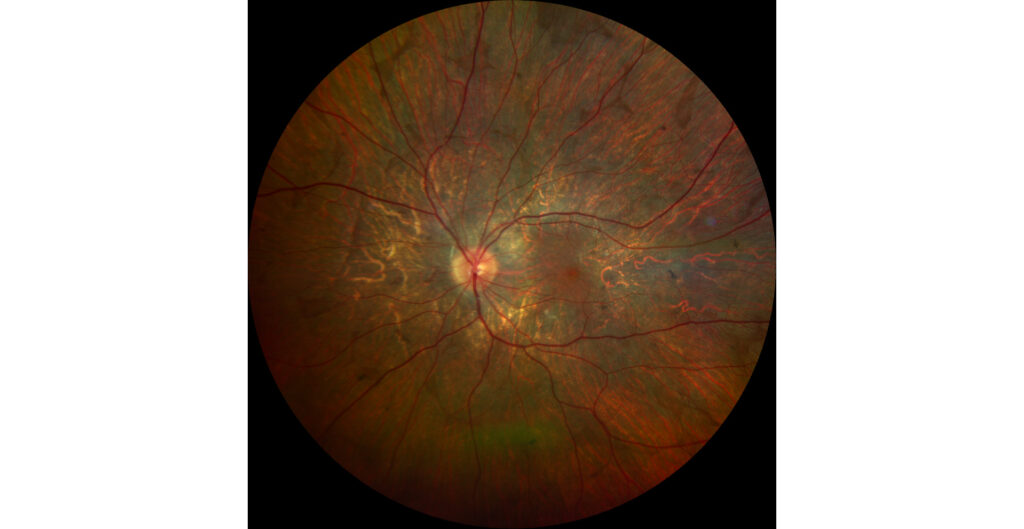
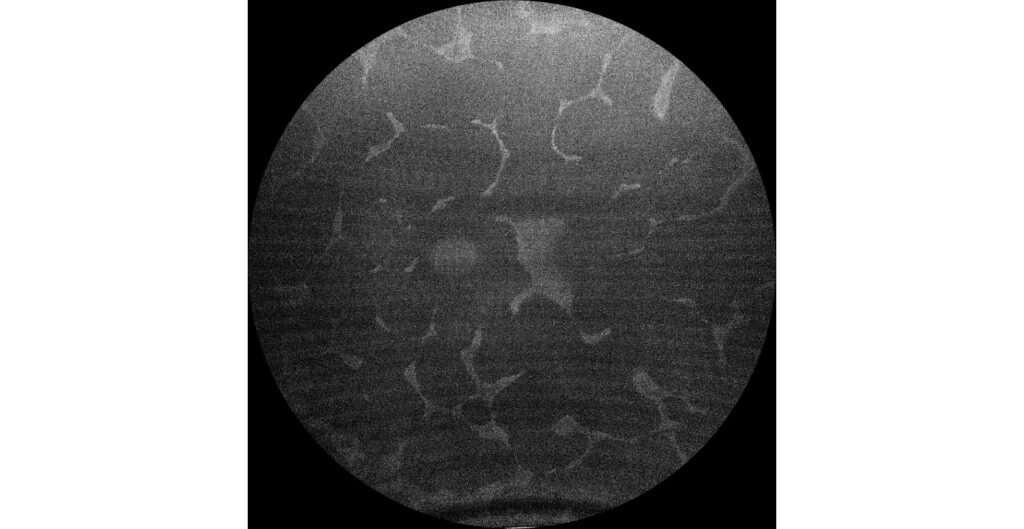
Green autofluorescence (Clarus 700, Zeiss): hypoautofluorescent areas corresponding to RPE atrophy predominate. Hyperautofluorescent areas correspond to healthy retina, including central areas that include the fovea (B1, B2).
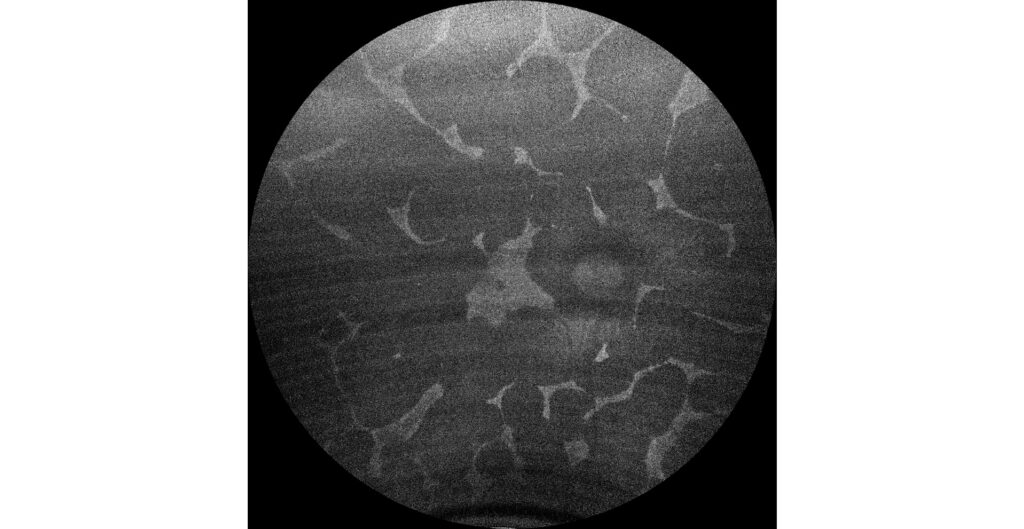
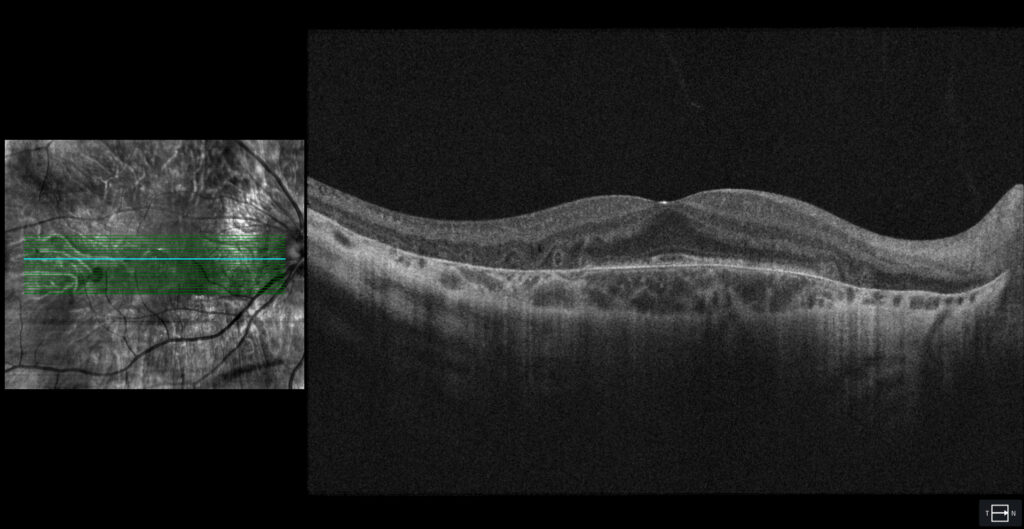
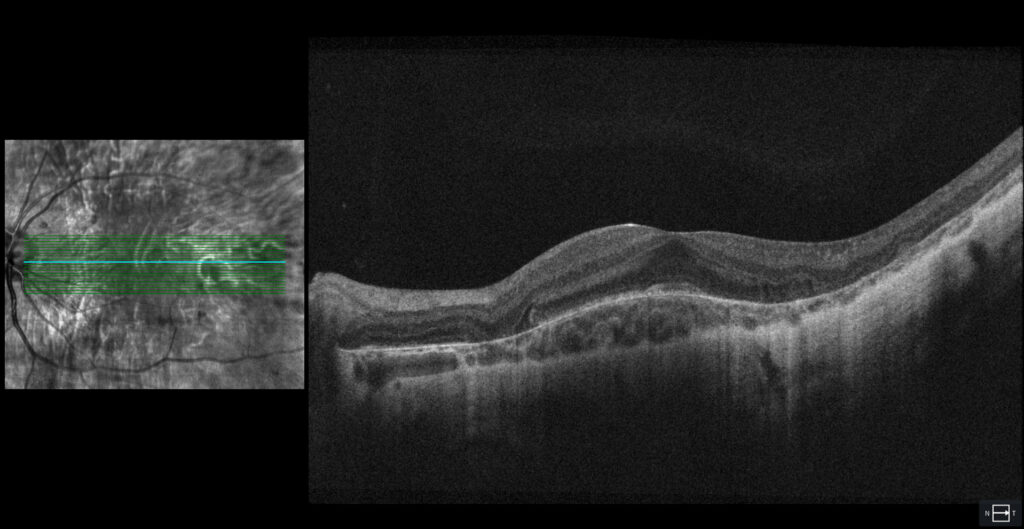
OCT (Cirrus 5000-HD, Zeiss): atrophy of RPE, choroid and outer retina except in the foveal and parafoveal areas (C1, C2). In the OCT of the RE, external retinal tubulations secondary to atrophy of the outer retina (C1) are observed.
Description
11-year-old male patient comes for a check-up.
VA OD 20/20 OS 20/25.
The fundus examination shows severe chorioretinal atrophy both in the periphery and macula, with preservation of a central island of healthy retina (which explains the patient’s good vision) and several remnants of healthy retina scattered in the periphery. Autofluorescence allows for better differentiation between areas of healthy retina and areas of atrophy in the retina, RPE, and choroid. The suspected diagnosis of choroideremia was genetically confirmed.