Toxoplasmosis
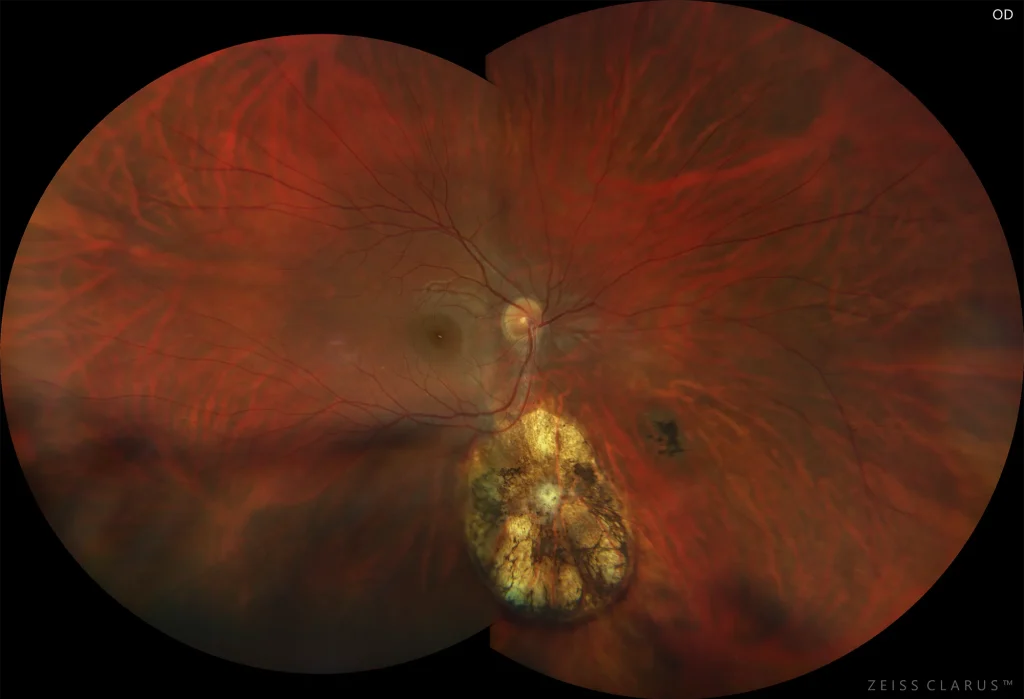
Figure 1. Color retinography of the right eye showing the inferior pigmented chorioretinal scar, myopic retinochoriodosis, and peripapillary atrophy.
Description
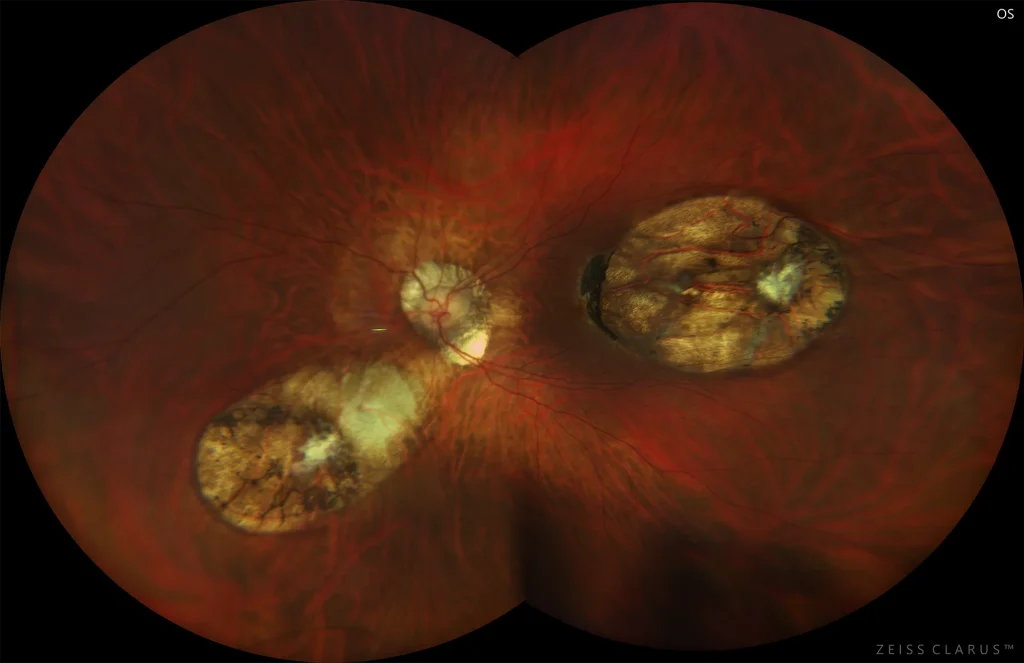
Toxoplasmosis is caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an intracellular protozoan. The definitive host is the cat, and intermediate hosts include humans, among others. Oocysts are excreted in feline feces and then ingested by the intermediate host in undercooked meat, eggs, or contaminated water supplies. It is also transmitted through the placenta in a woman with active toxoplasmosis. In immunocompetent patients, primary infection is usually subclinical. Regarding ocular manifestations, recurrent episodes of inflammation due to rupture of cysts are frequent. It may cause granulomatous anterior uveitis. The presence of an isolated white and fringed inflammatory focus of retinochoriodosis associated with a pigmented scar is typical. De novo foci not associated with an old scar and multiple lesions are rare in immunocompetent patients, but frequent in immunosuppressed patients. It may cause retinal vasculitis and papilledema. Diagnosis is usually based on clinical examination findings.