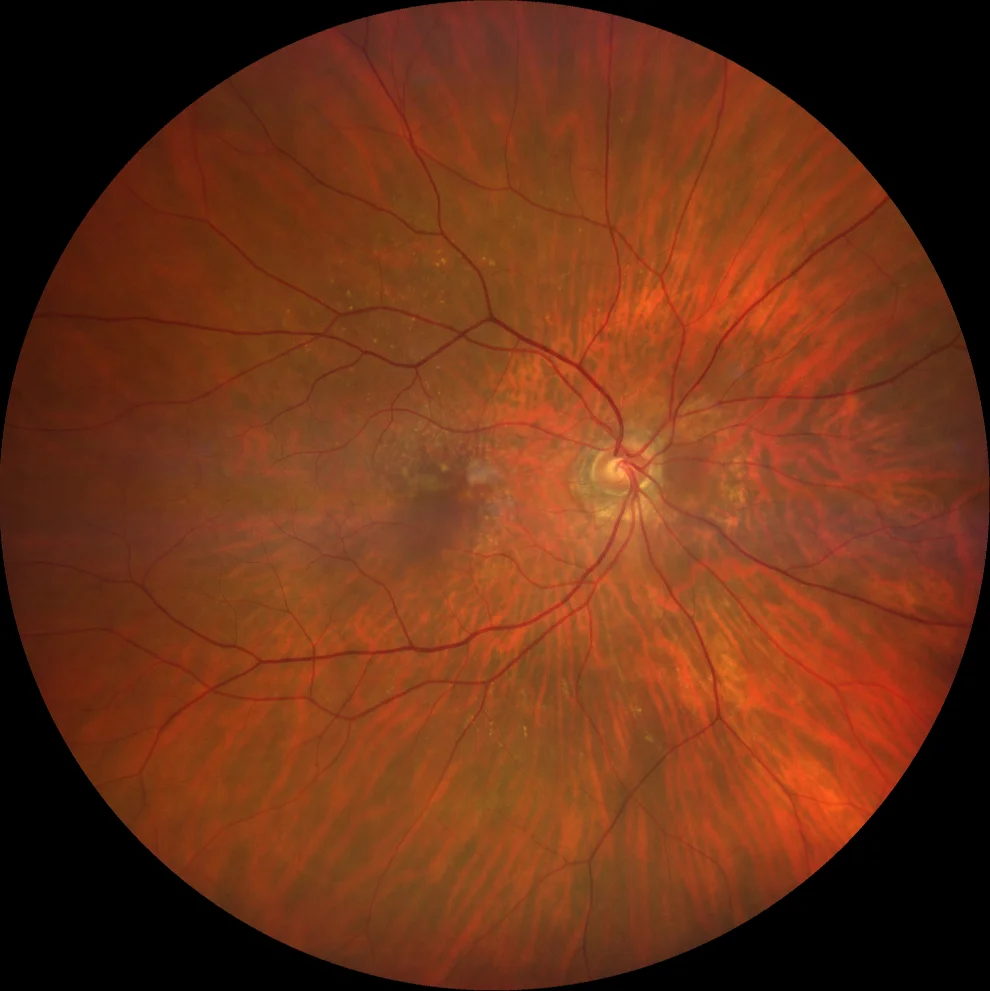
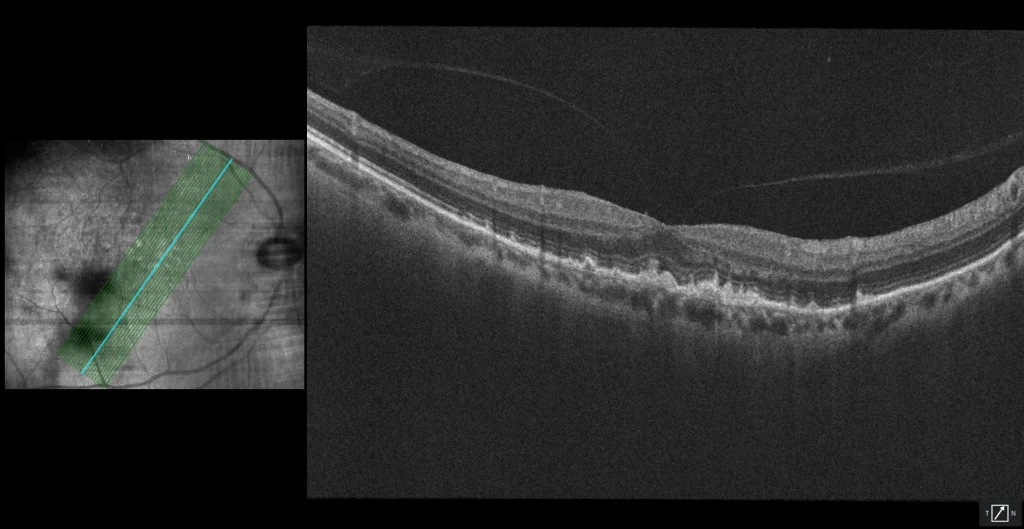
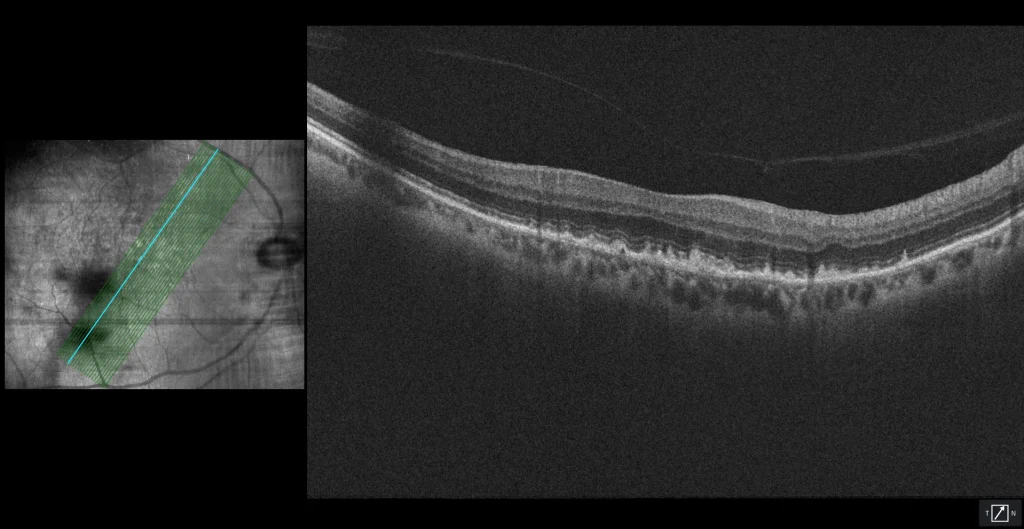
Subretinal drusenoid deposits
A: SDD are numerous yellowish punctate deposits that have a predilection for the upper macula (where there is a higher density of rods).
B1, B2: both in the foveal section (B1) and in a more temporal section (B2), hyperreflective deposits are observed above the RPE (hence their name pseudodrusen) in stages 2 (undulation of the EZ line) and 3 (erosion of the EZ and even of the MLE). The most useful test to detect SDD is near-infrared reflectance, as can be seen in the boxes on the left of both OCTs.
B1, B2: both in the foveal section (B1) and in a more temporal section (B2), hyperreflective deposits are observed above the RPE (hence their name pseudodrusen) in stages 2 (undulation of the EZ line) and 3 (erosion of the EZ and even of the MLE). The most useful test to detect SDD is near-infrared reflectance, as can be seen in the boxes on the left of both OCTs.
Description
76-year-old woman with minimal vision loss in her right eye who comes for a check-up.
AVMC OD 20/30 OI 20/20
Reticular pseudodrusen and soft drusen in AO (OD shown).