Central retinal vein occlusion
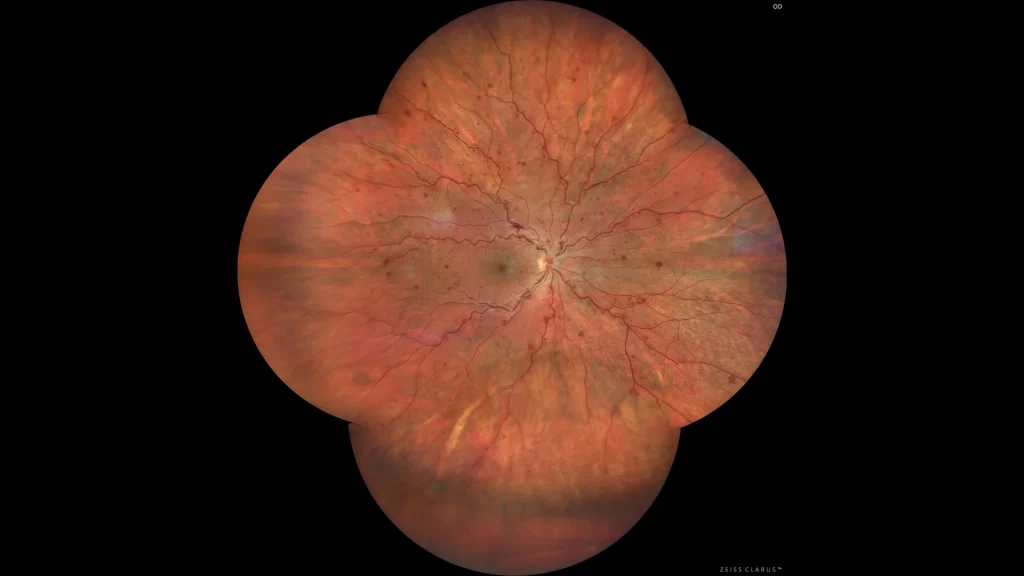
Color retinography showing intraretinal hemorrhages scattered in the 4 quadrants, as well as venous tortuosity and engorgement. Choroidal vascular atrophic changes are also seen in the lower periphery.
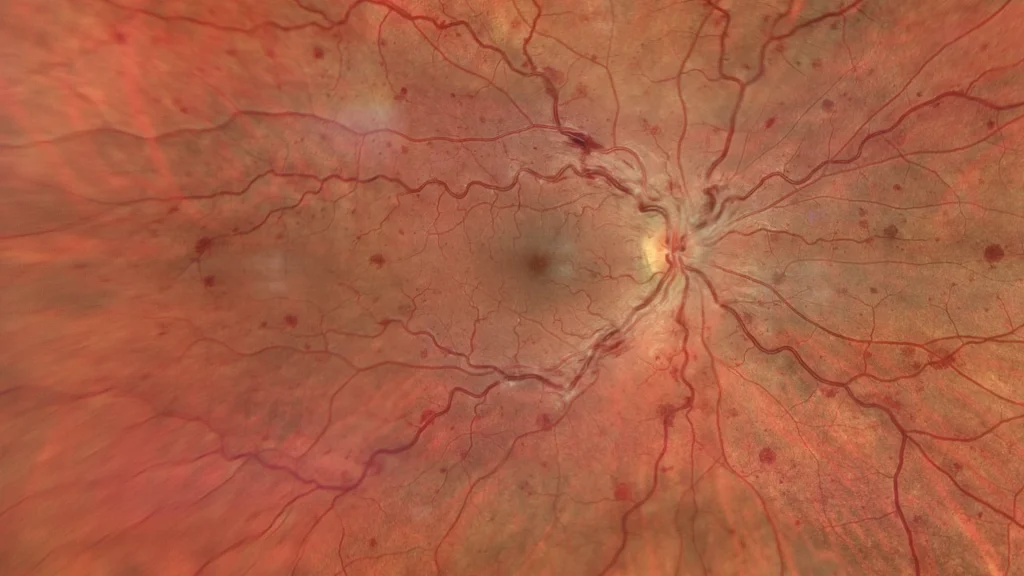
Enhanced color retinography in the posterior pole where vascular tortuosity, retinal hemorrhages, and perivascular cotton-wool exudates indicating probable ischemia are observed with greater definition.
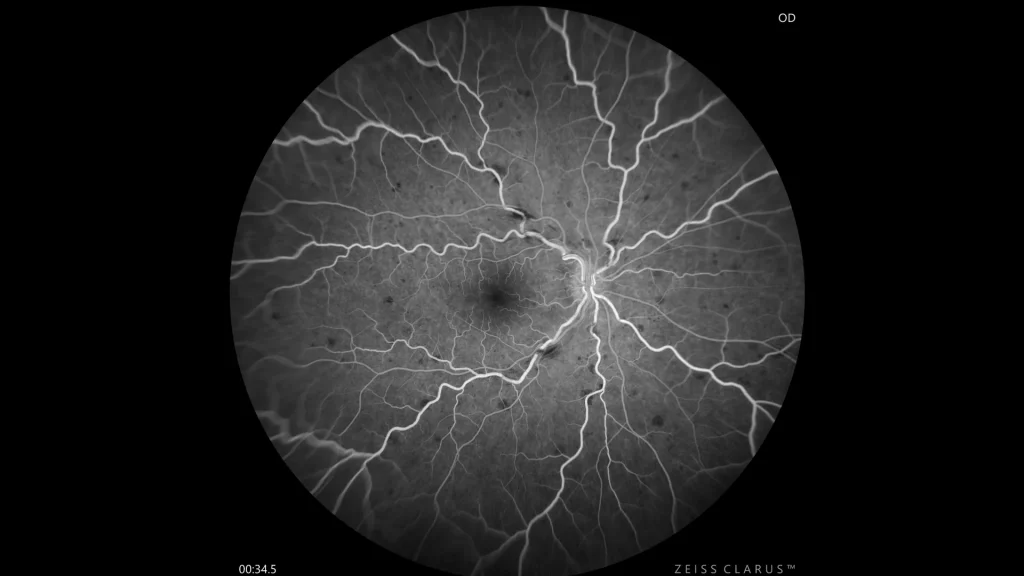
Fluorescein angiography: During late venous filling, good vascular perfusion is seen throughout the retina. There is no macular edema or significant perimacular vascular permeability. Defects are secondary to scattered hemorrhages.
Description
Central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) is a blockage in the central vein of the retina, usually due to atherosclerosis, hypertension, or diabetes. On fundusography, hemorrhages in all four quadrants, retinal edema, and venous dilation are seen. Advanced complications include neovascularization and neovascular glaucoma. Treatment may include intravitreal injections of anti-angiogenics, corticosteroids, and laser photocoagulation to manage macular edema and neovascularization.