< back
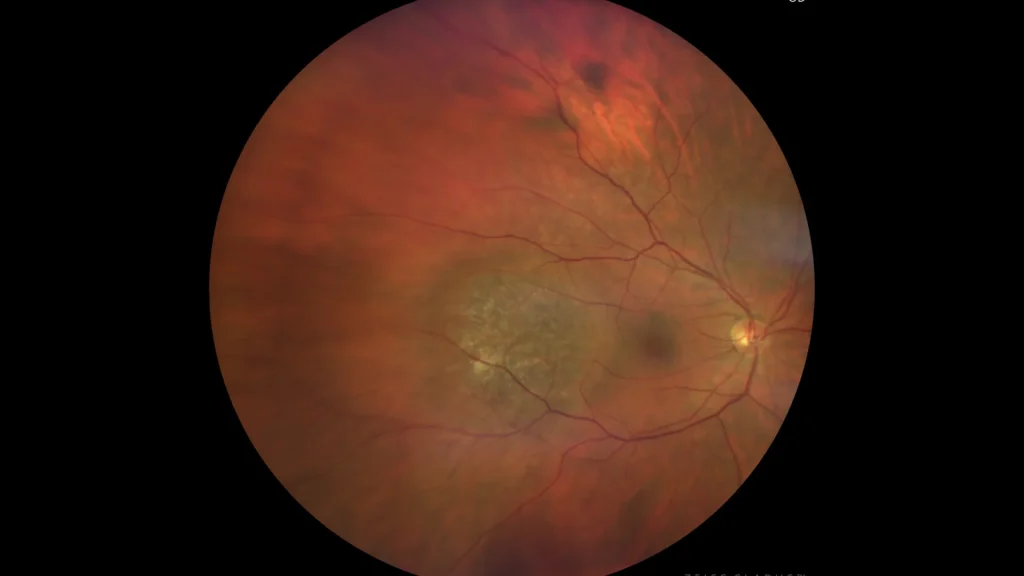
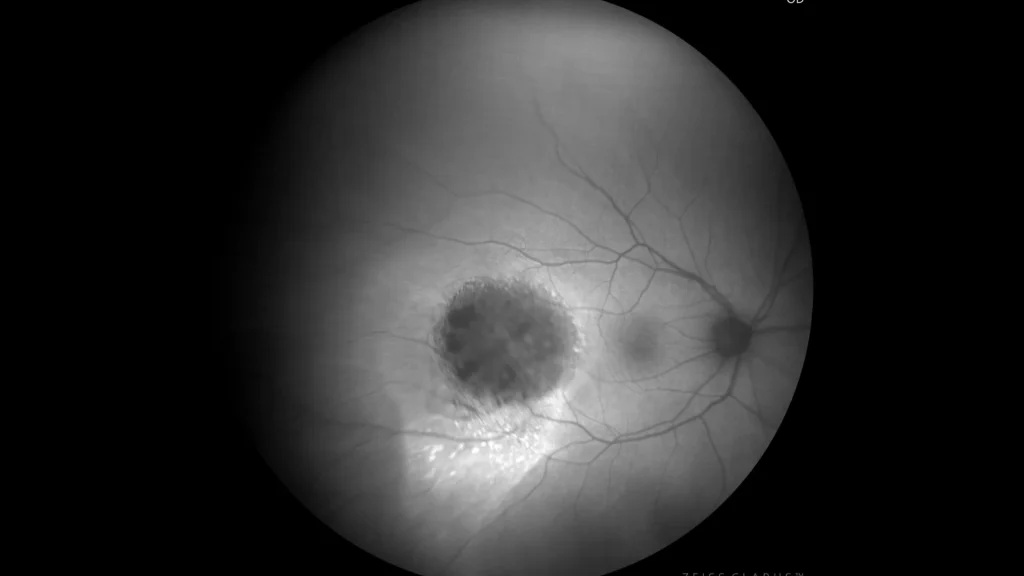
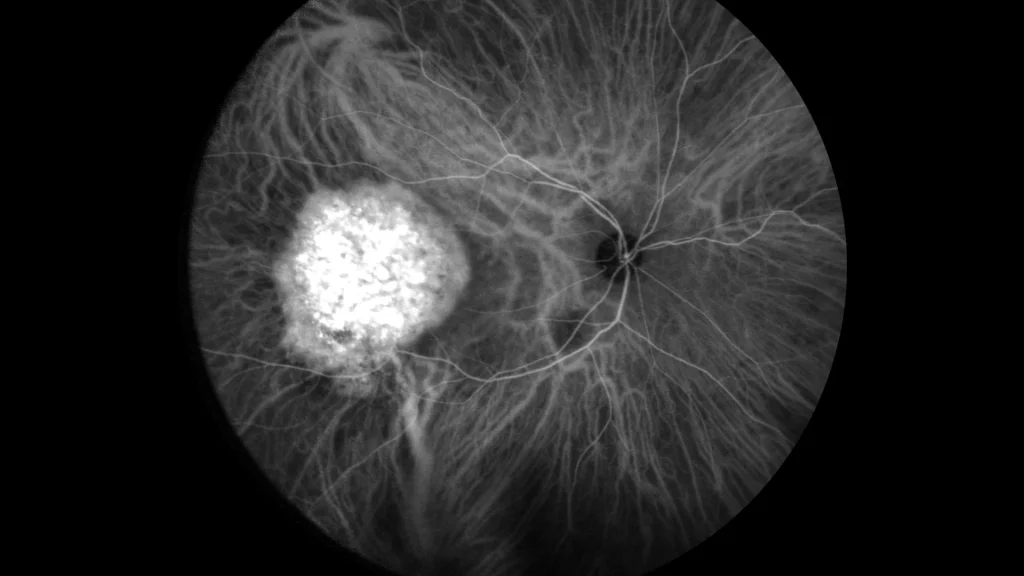
Choroidal Hemangioma
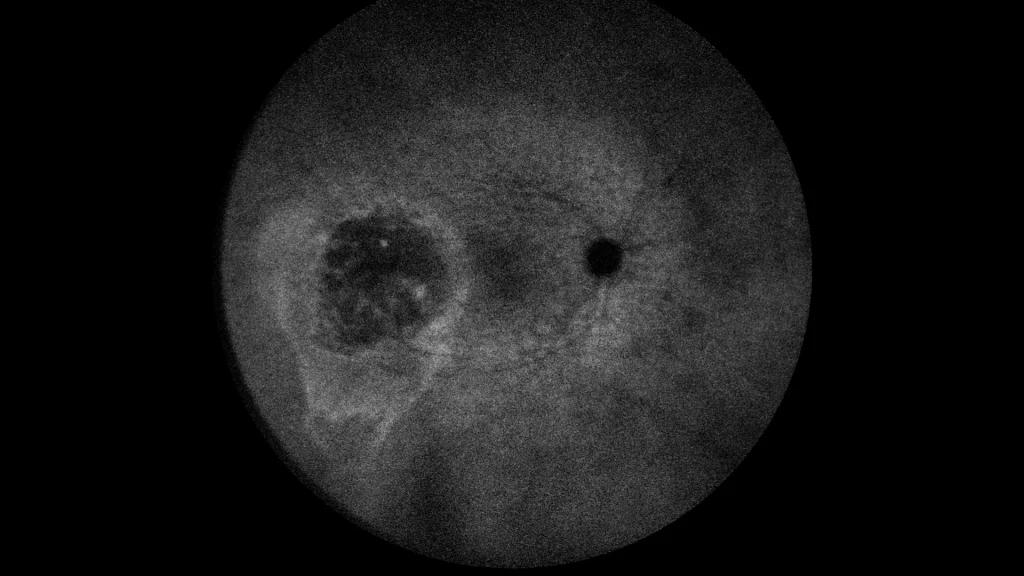
Green autofluorescence: the lesion is shown with hypoautofluorescence, and with a hyperautofluorescent gravitational trail image
Description
Choroidal hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor. It presents as a localized or diffuse tumor. Localized choroidal hemangioma is usually detected in midlife, when it begins to cause symptoms such as photopsia, floaters, or decreased visual acuity. The decrease in visual acuity is due to associated progressive hyperopia, subretinal fluid, macular edema, or retinal atrophy.