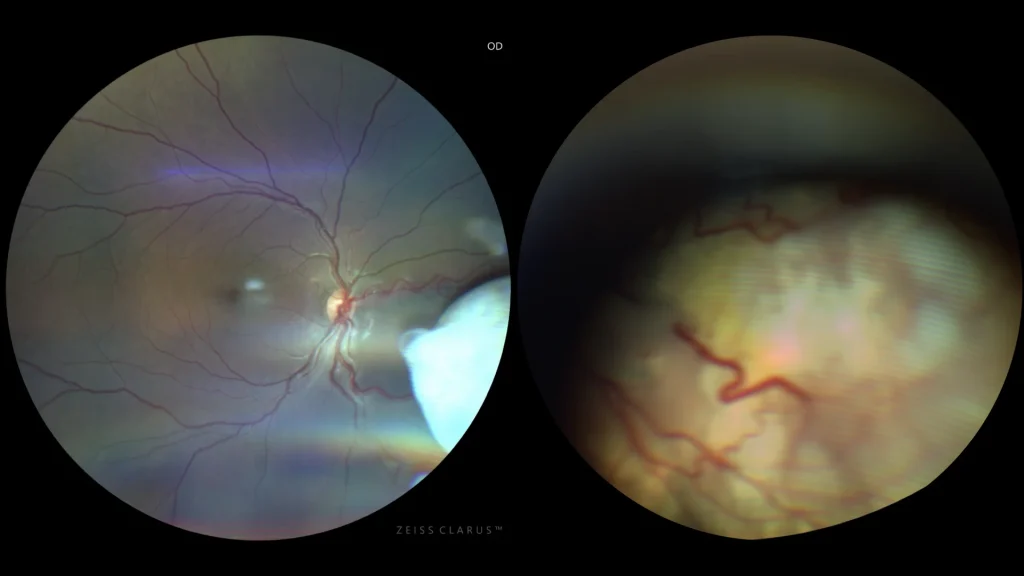
Retinoblastoma
Right eye color: It shows a white or cream-colored mass, dense and possibly with calcifications, which gives it a chalky appearance. The surrounding retinal vessels are visible, deviating towards the tumor. ๏ Left eye color: Tumor-like elevation of the retina of the left eye with a yellowish white color, greater exudative component, and severe destructuring of the posterior pole.
Description
Retinoblastoma is a malignant tumor of the retina that predominantly occurs in childhood, being the most common ocular tumor in children. The most common clinical symptoms include leukocoria, strabismus, and vision loss. During ophthalmoscopic examination, a whitish lesion on the retina that is characteristic of retinoblastoma can be seen. Ocular ultrasound typically reveals an intraocular mass with calcifications, and computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used to assess the extent of the tumor and rule out extraocular spread. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to improve survival rates and preserve vision. Timely intervention can also prevent metastatic spread, which is most common to the brain and bones, thereby improving long-term visual and life outcomes for affected patients.