< back
Tumors of the retina and choroid
Description
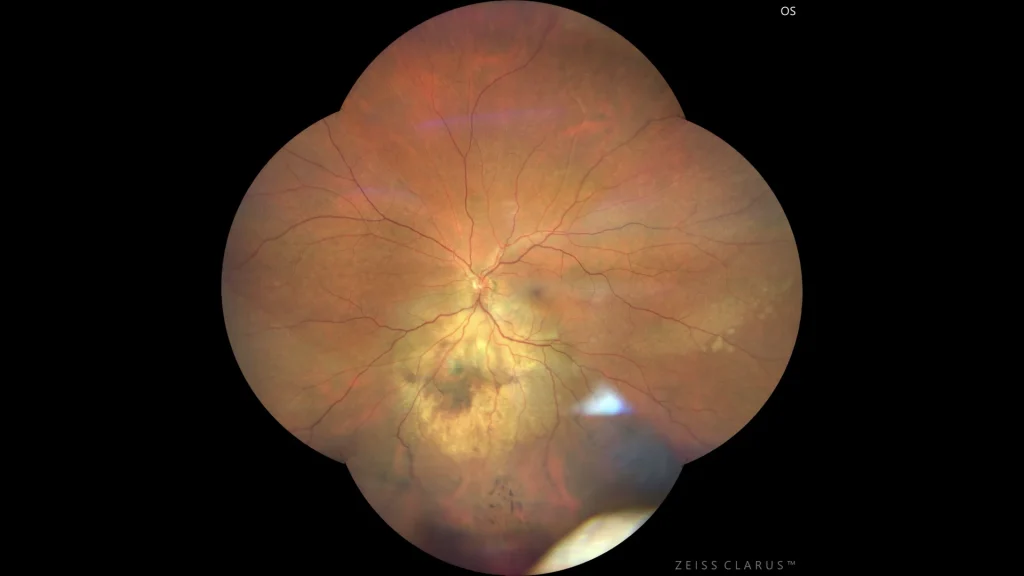
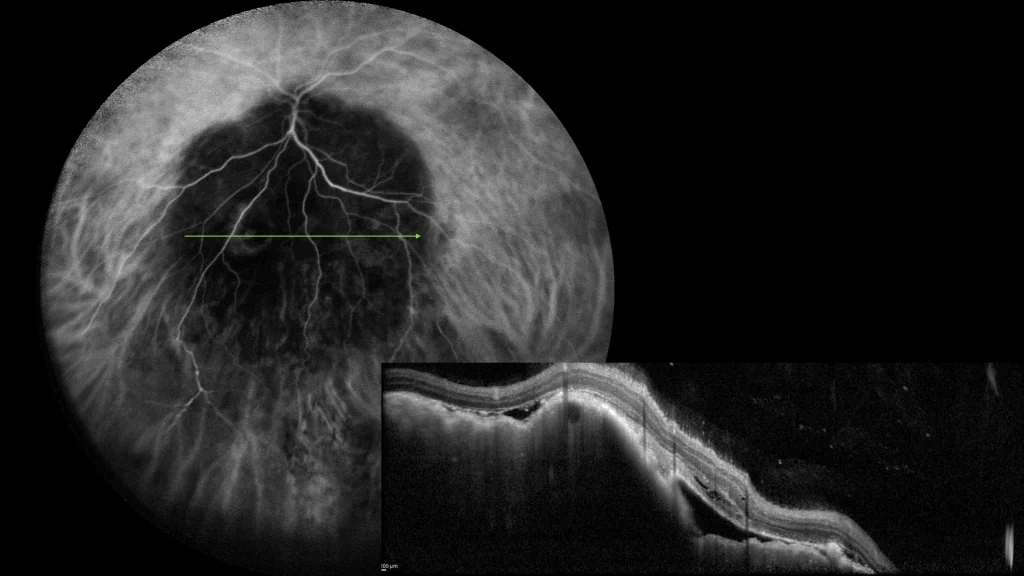
Choroidal metastases are the most common form of intraocular neoplasia in adults, frequently originating from breast and lung neoplasias. Patients may present with visual symptoms or be asymptomatic. Diagnosis is made through fundus examinations and imaging techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) or ultrasound. Treatment depends on the primary neoplasia and includes systemic and local therapies such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, seeking to preserve vision and improve quality of life. The detection of choroidal metastases indicates advanced disease, with a reserved prognosis.