Aneurysmal neovascularization type 1
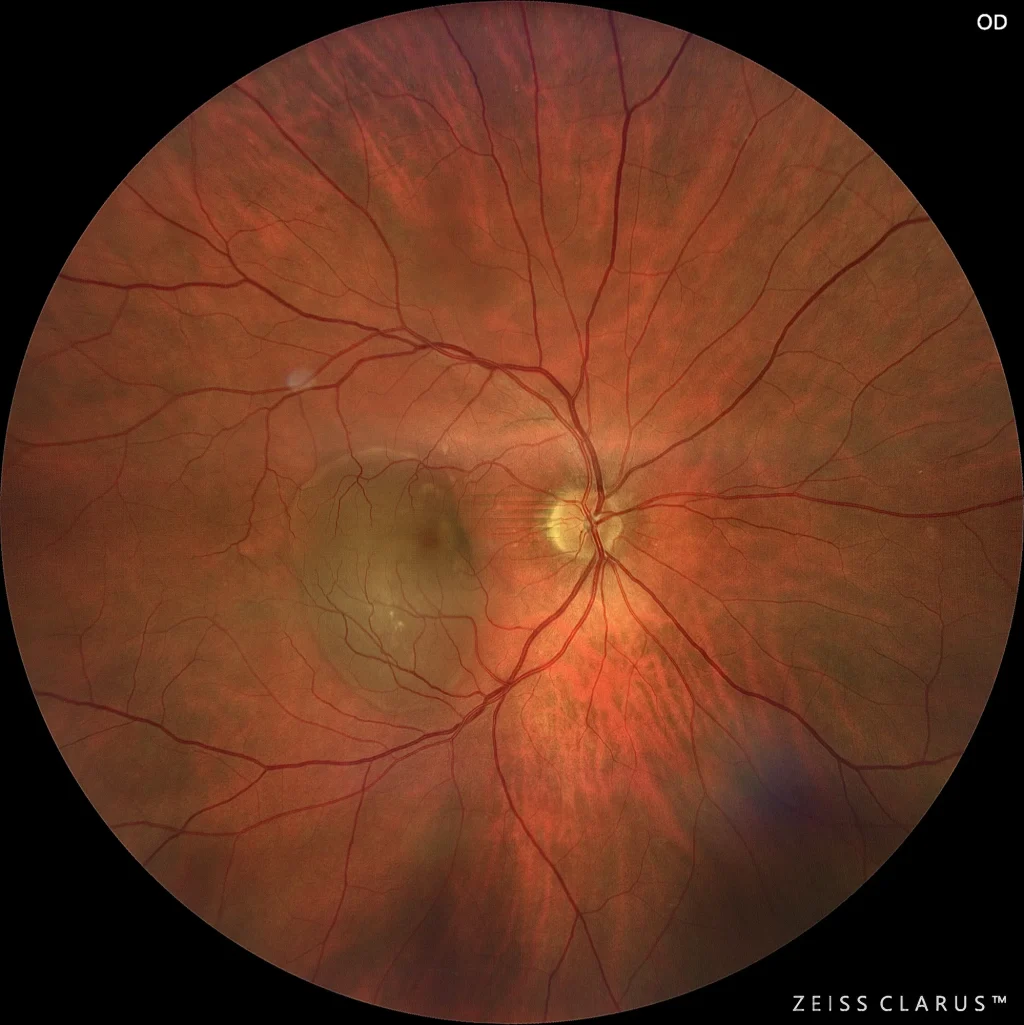
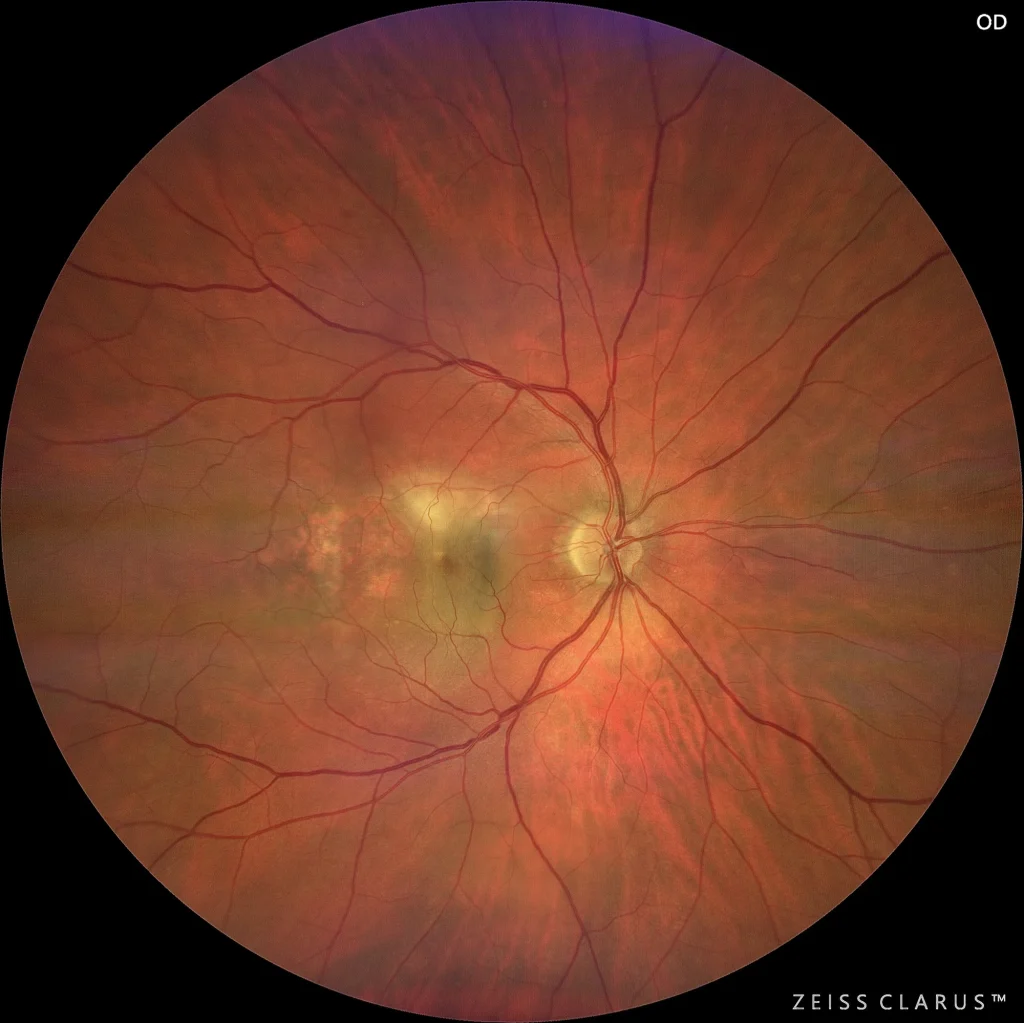
Color retinography showing an abrupt lifting of the pigmented epithelium, with a grayish tone and well-defined edges.
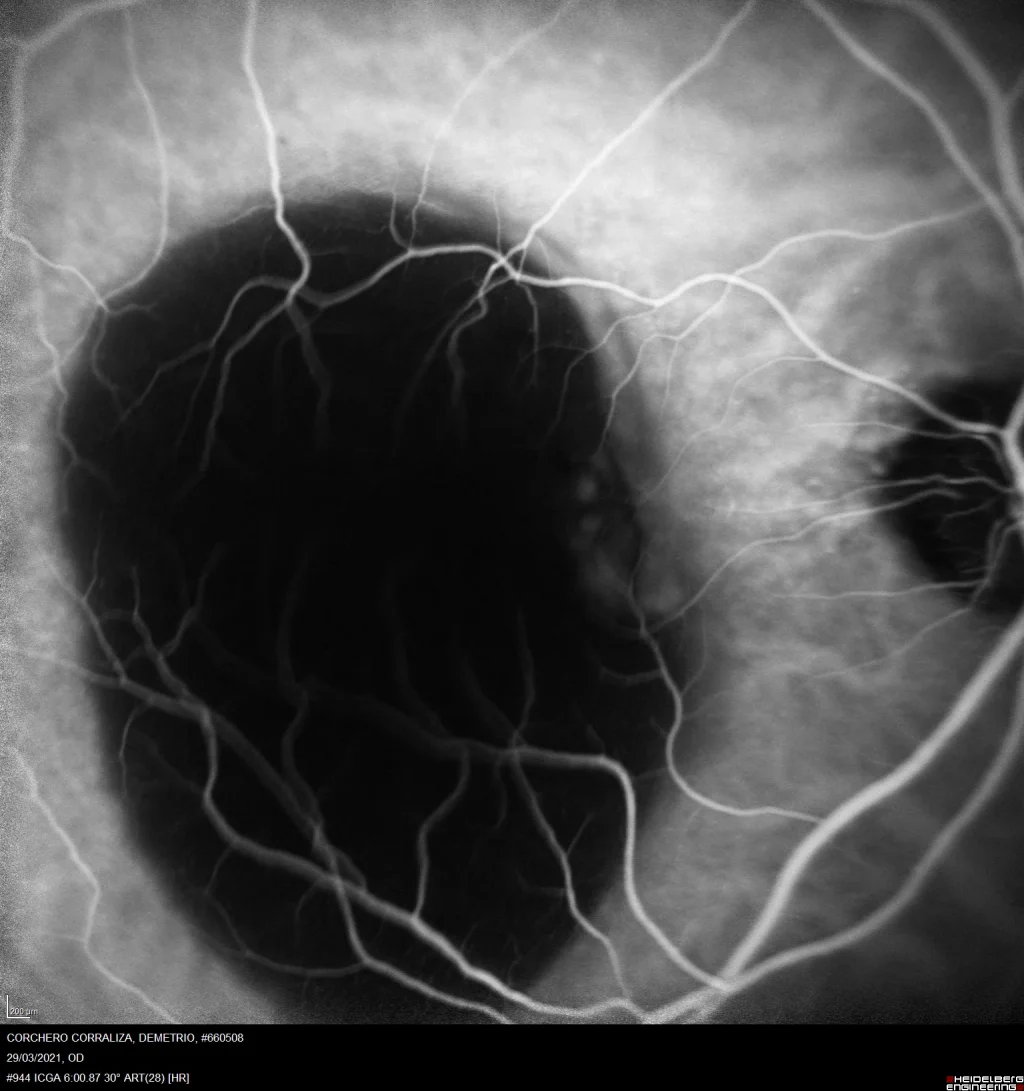
Indocyanine green angiography Spectralis: The AVI shows a hypocyanescent lesion that coincides with the PED, and its nasal margin is notable for the presence of hypercyanescent bouquet formations, which constitute the VCP.
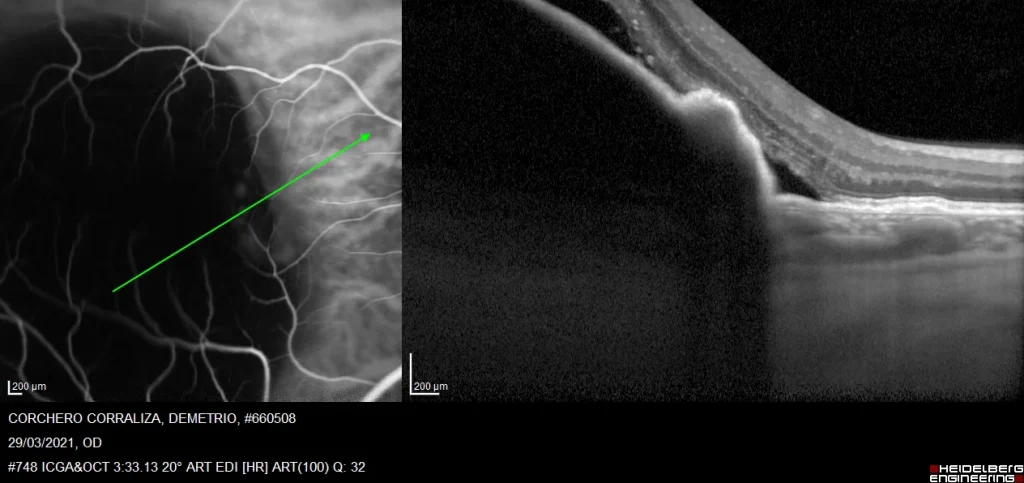
3. Optical coherence tomography. The OCT shows a wide and convex PED, where we observe an irregular protrusion at its nasal end, and just below the RPE a rounded hyperreflective lesion stands out, which constitutes the aneurysmal dilatation or polyp.
Description
Aneurysmal neovascularization type 1, also known as polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV), is a condition characterized by the presence of sub-pigmented epithelial neovessels with aneurysmal or polypoidal dilatations. This entity is within the spectrum of pachychoroidal diseases.