Oculocutaneous albinism
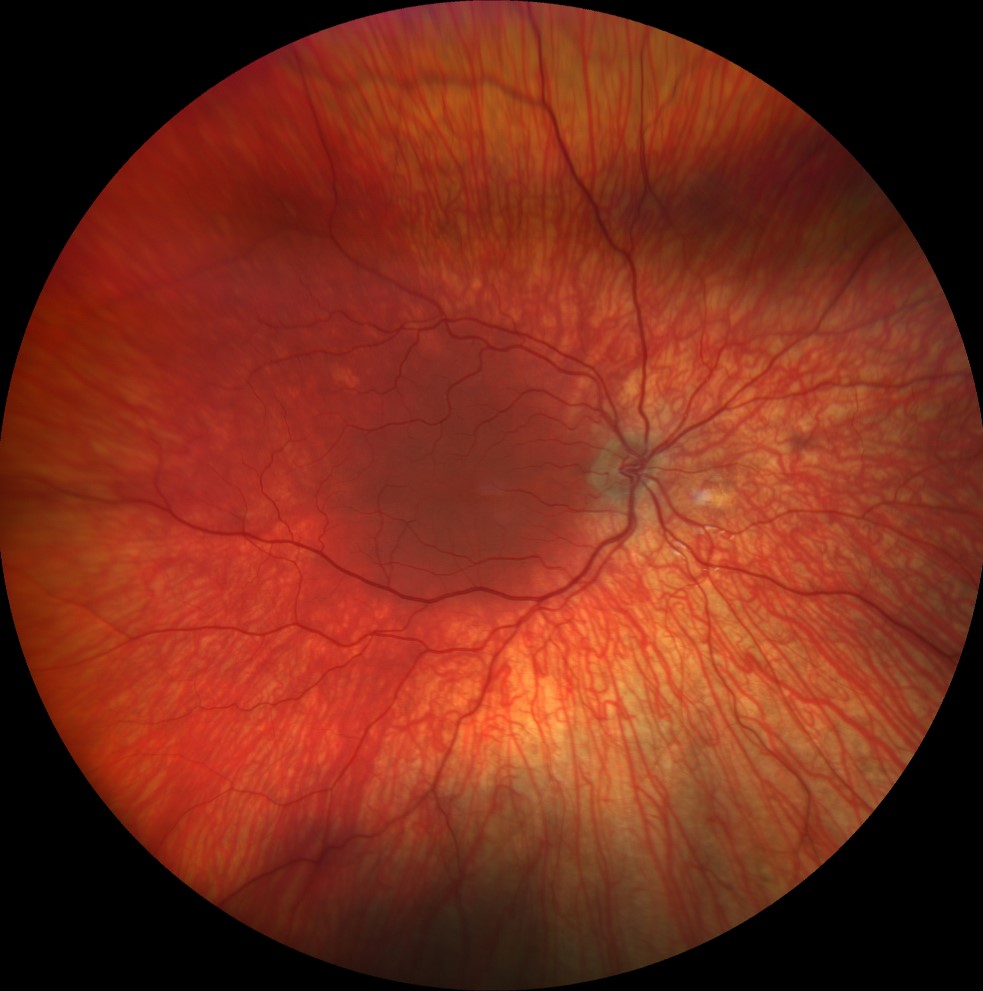
Color retinography (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss) of the right and left eyes, showing bilateral choroidal hypopigmentation, allowing good visualization of the choroidal vascularization
Color retinography (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss) of the right and left eyes, showing bilateral choroidal hypopigmentation, allowing good visualization of the choroidal vascularization
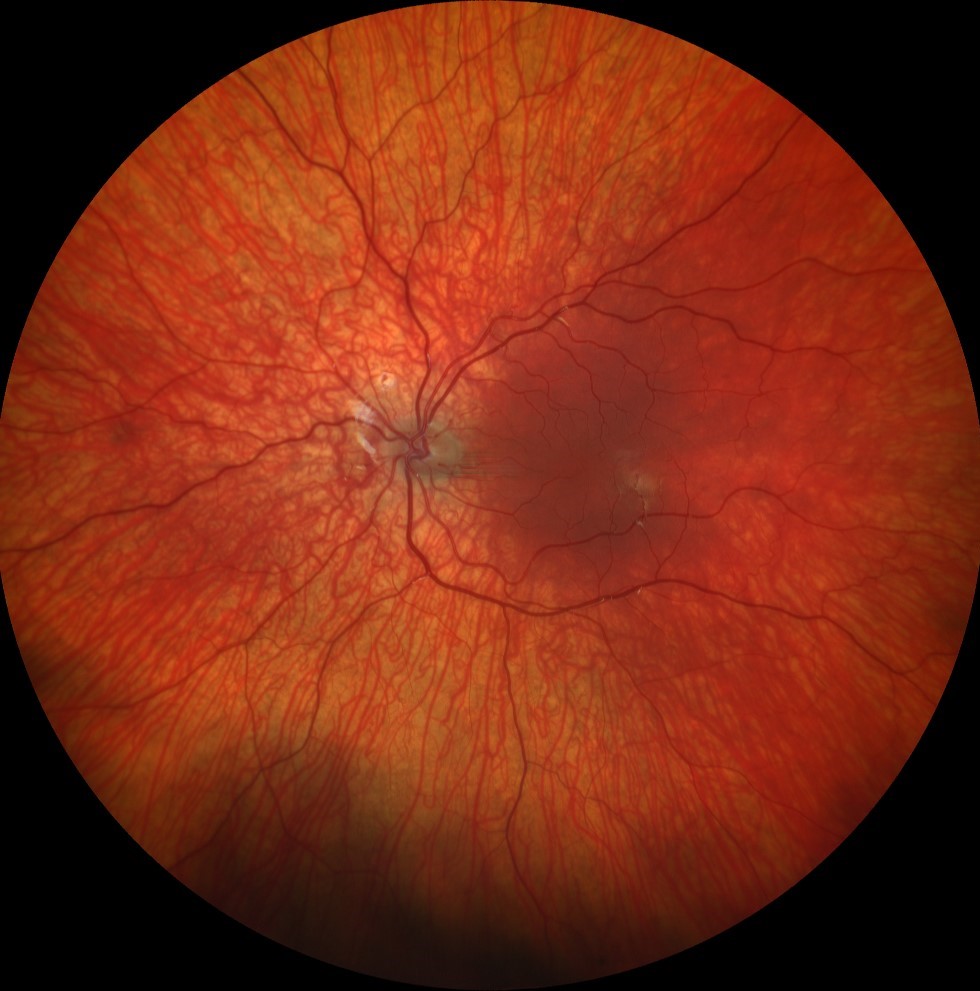
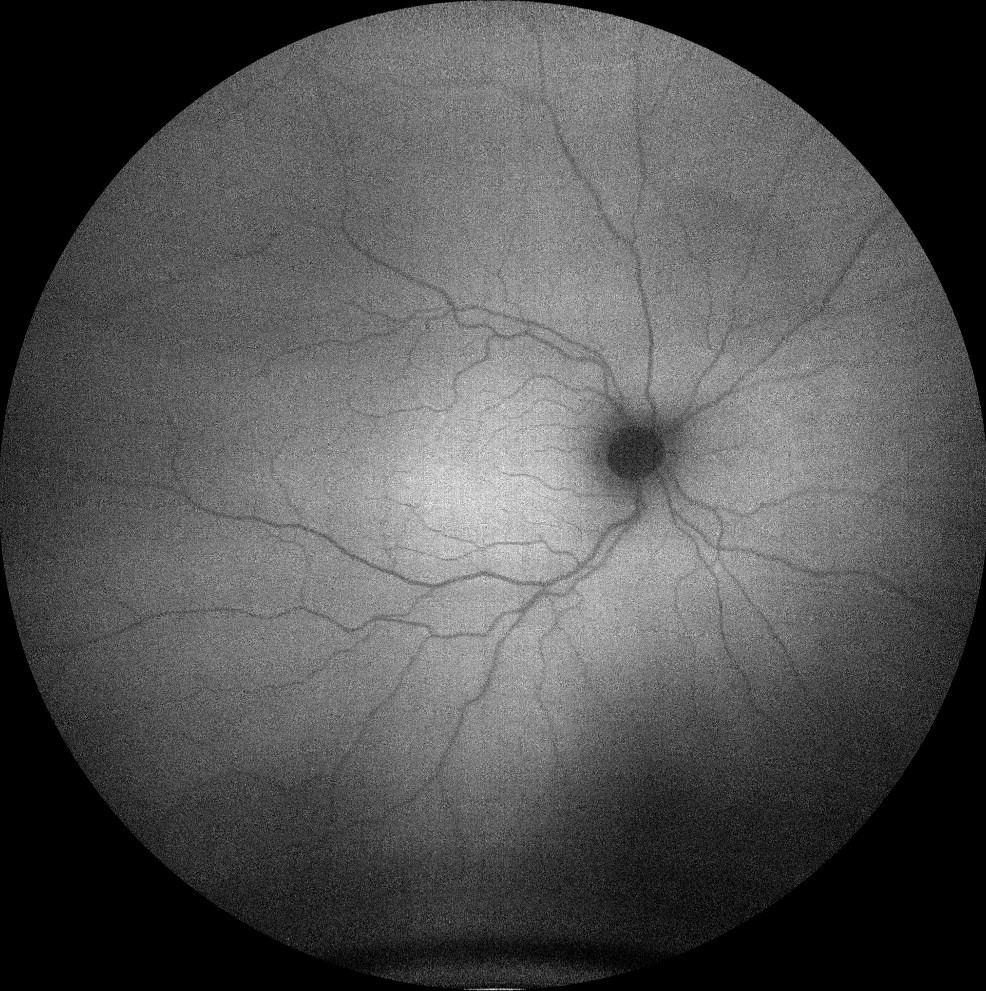
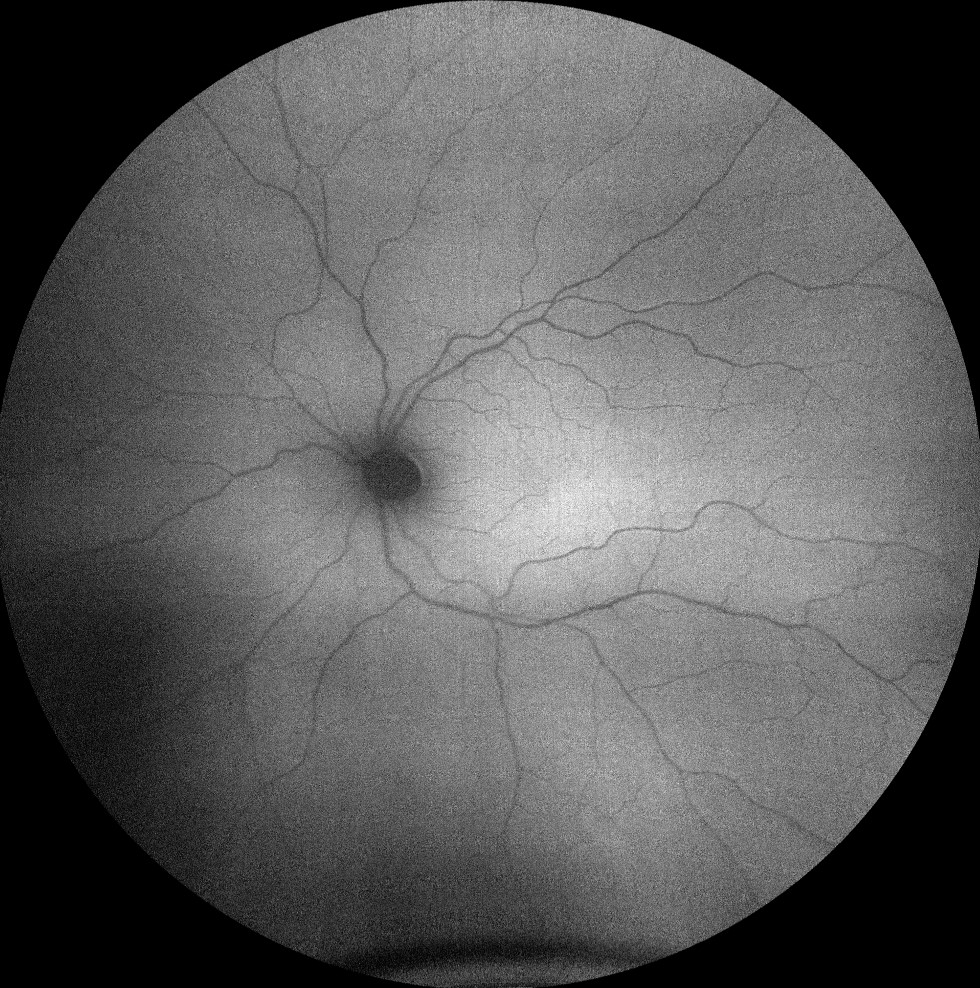
Autofluorescence images (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss) of the right and left eyes, showing an absence of normal foveal hypoautofluorescence
Autofluorescence images (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss) of the right and left eyes, showing an absence of normal foveal hypoautofluorescence
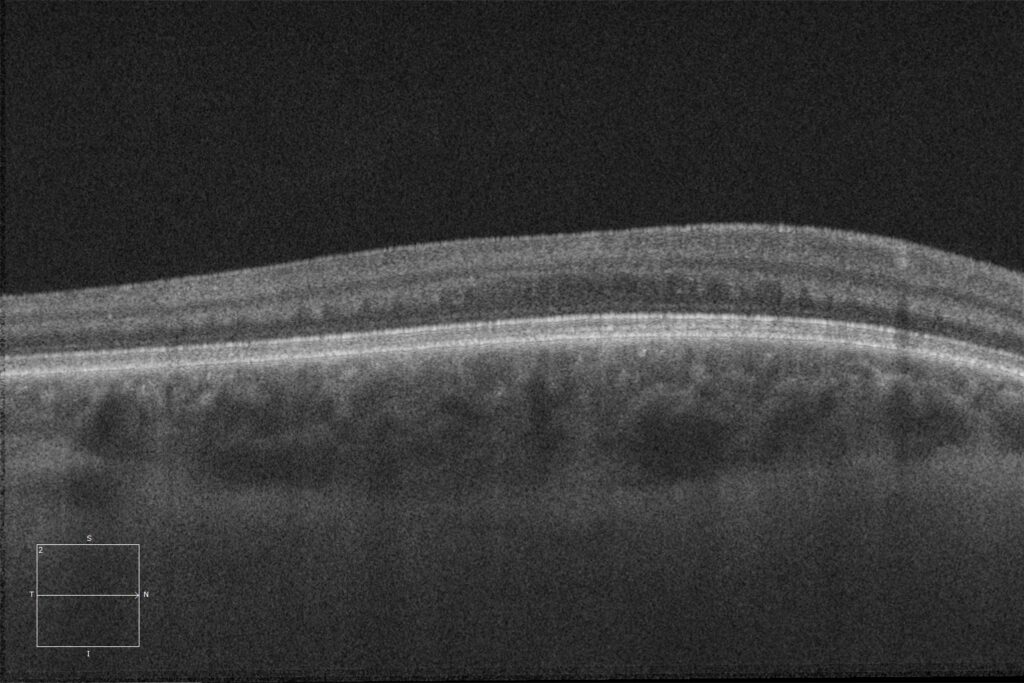
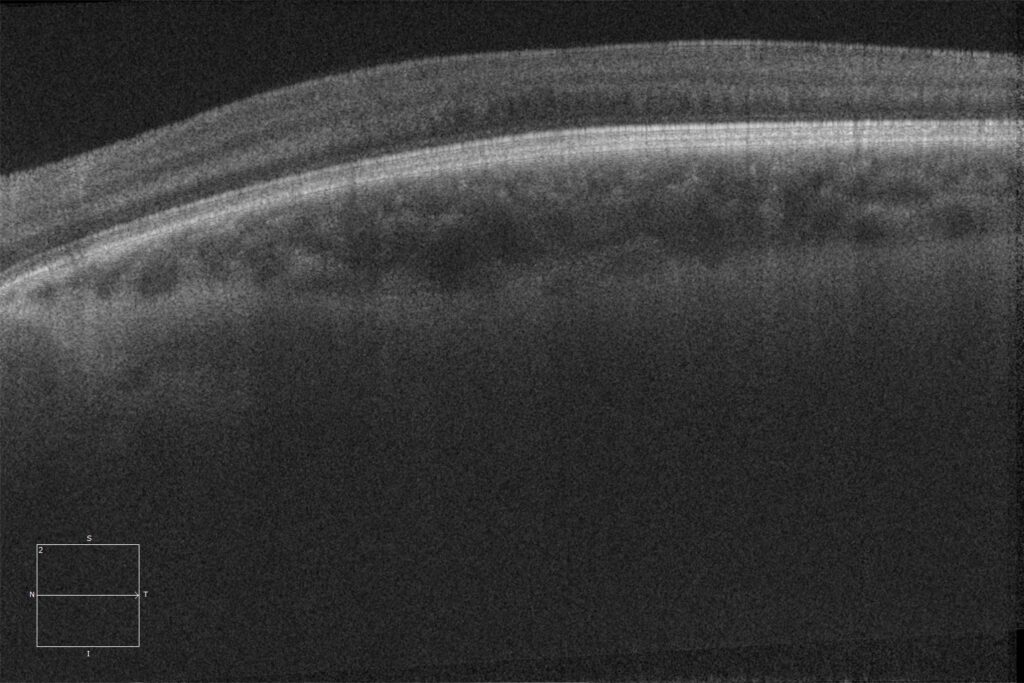
Macular HD optical coherence tomography (Cirrus 5000, Carl Zeiss) of the right and left eyes, showing the absence of the normal foveal depression, with the presence of inner retinal layers in the area where the fovea should be (foveal hypoplasia).
Description
Albinism is a genetic disorder characterized by hypopigmentation, both cutaneous and ocular, due to impaired melanin biosynthesis. There are oculocutaneous and isolated ocular forms (less frequent). The seven variants of oculocutaneous albinism are inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and affect both sexes equally. The two variants with exclusive ocular involvement are inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern.
In addition, there are two syndromic forms of oculocutaneous albinism: Chédiak-Higashi (which is associated with congenital immunodeficiency) and Hermansky-Pudlak (which is associated with bleeding due to platelet abnormalities). These two forms also have autosomal recessive inheritance.
At the ocular level, albinism is characterized by hypopigmentation of the iris with transillumination defects, hypopigmentation of the retinal pigment epithelium, foveal hypoplasia, and congenital nystagmus.
The diagnosis is clinical, although genotyping helps to define the specific subtype of the disease.