Branch venous occlusion
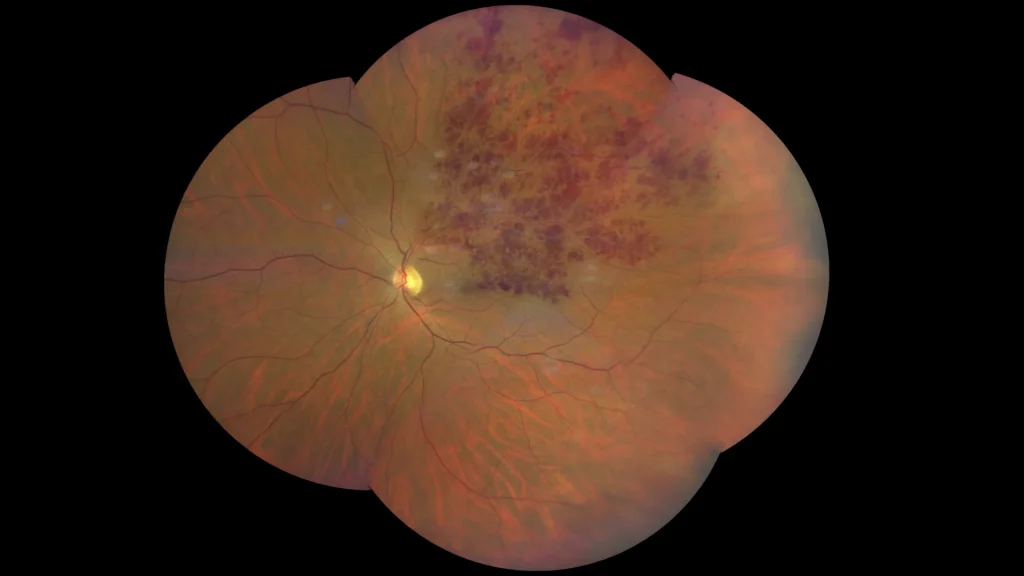
Color retinography showing exudates and scattered intraretinal hemorrhages accompanying the upper temporal arch.
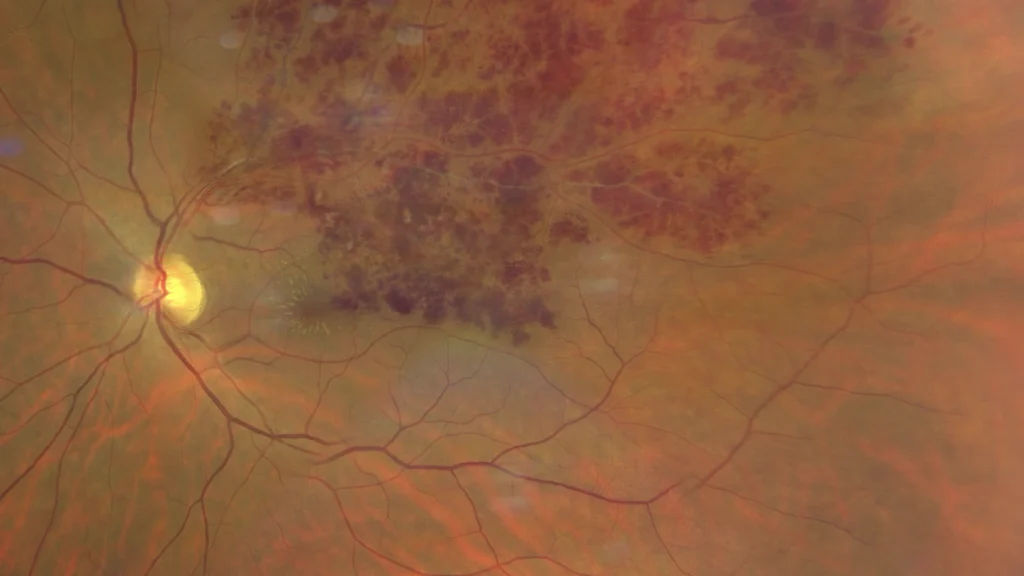
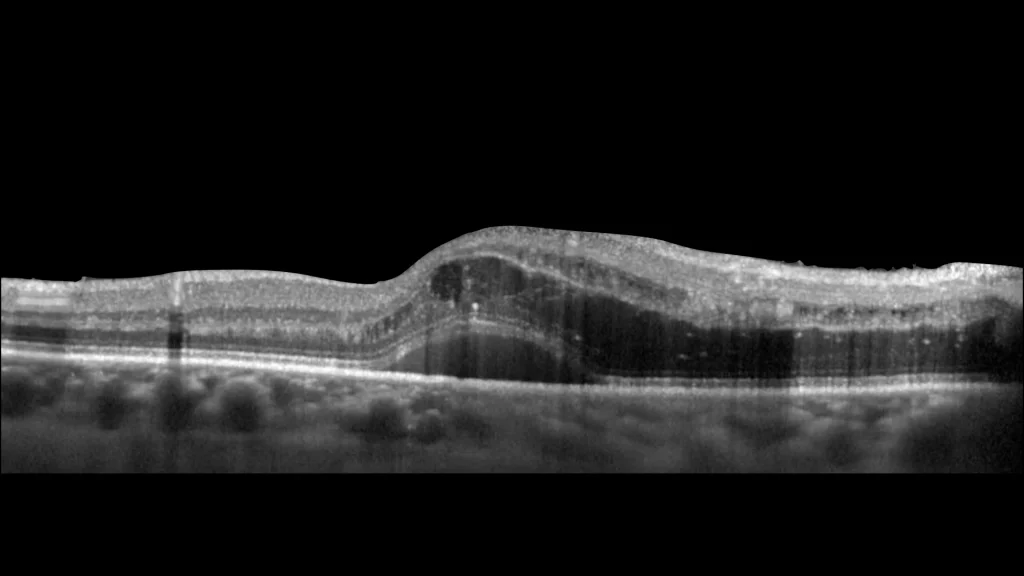
Color retinography enhanced in the posterior pole where some lipid exudates around the macula and the partially hyalinized vein are also observed.
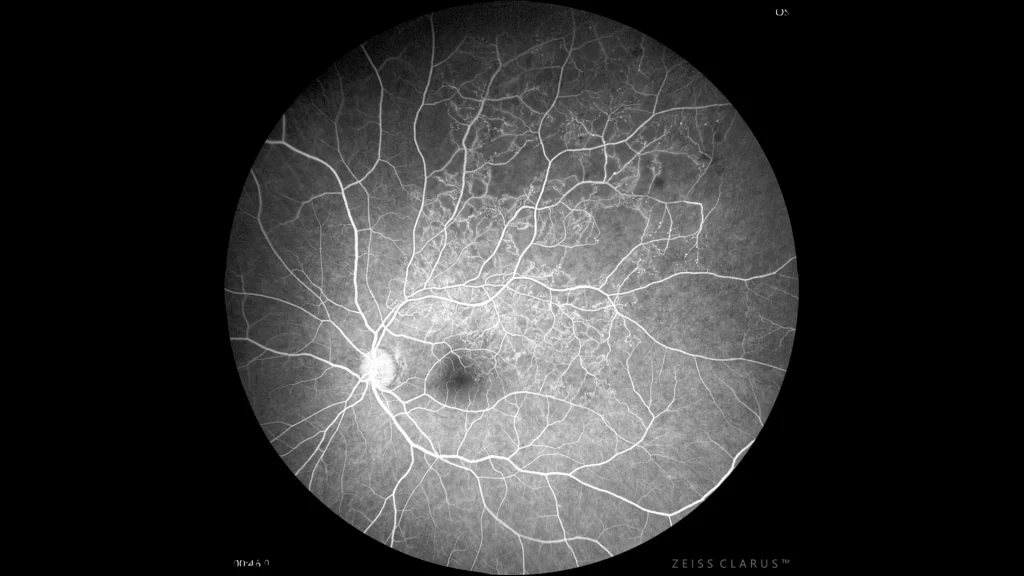
Fluorescein angiography showing abundant microvascular abnormalities, such as telangiectatic vessels, and microaneurysm-like hyperfluorescent points. A significant perfusion deficit in the upper temporal arch is also noted, which delimits a clear area of ischemia.
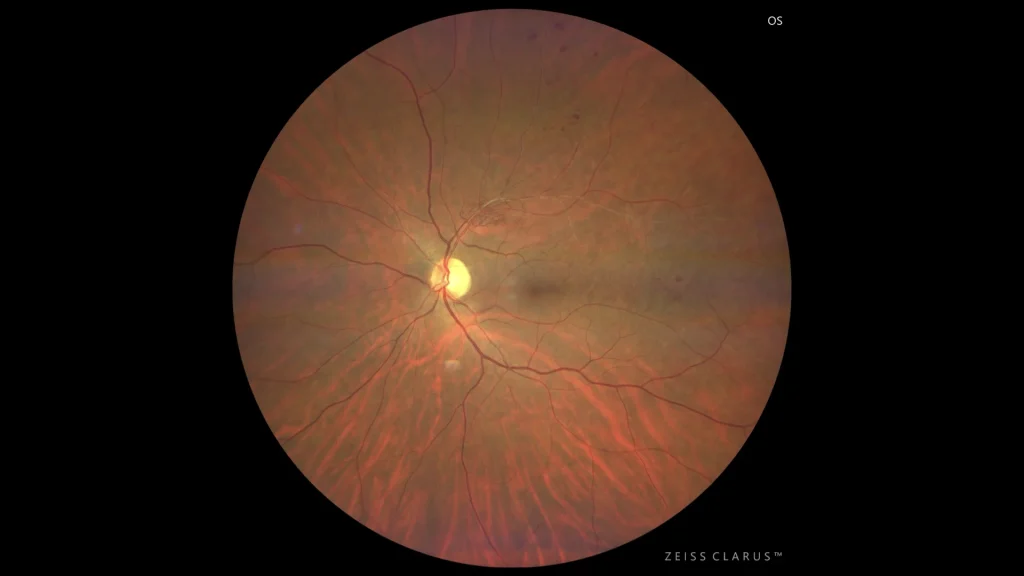
Colored retinography showing the same patient 18 months after starting treatment with anti-angiogenic agents. The presence of secondary vascular shunts bordering the venous occlusion is notable.
Description
Branch vein occlusion (BVO) is characterized by blockage of a retinal vein, usually due to atherosclerosis, hypertension, or diabetes. Findings on fundusography include intraretinal hemorrhages, retinal edema, and hard exudates. In advanced stages, neovascularization may occur, especially in ischemic forms. Treatment may range from observation to intravitreal injections of anti-angiogenics, corticosteroids, or laser photocoagulation, depending on the severity and the presence of complications such as macular edema or neovascularization.