Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy (FEVR)
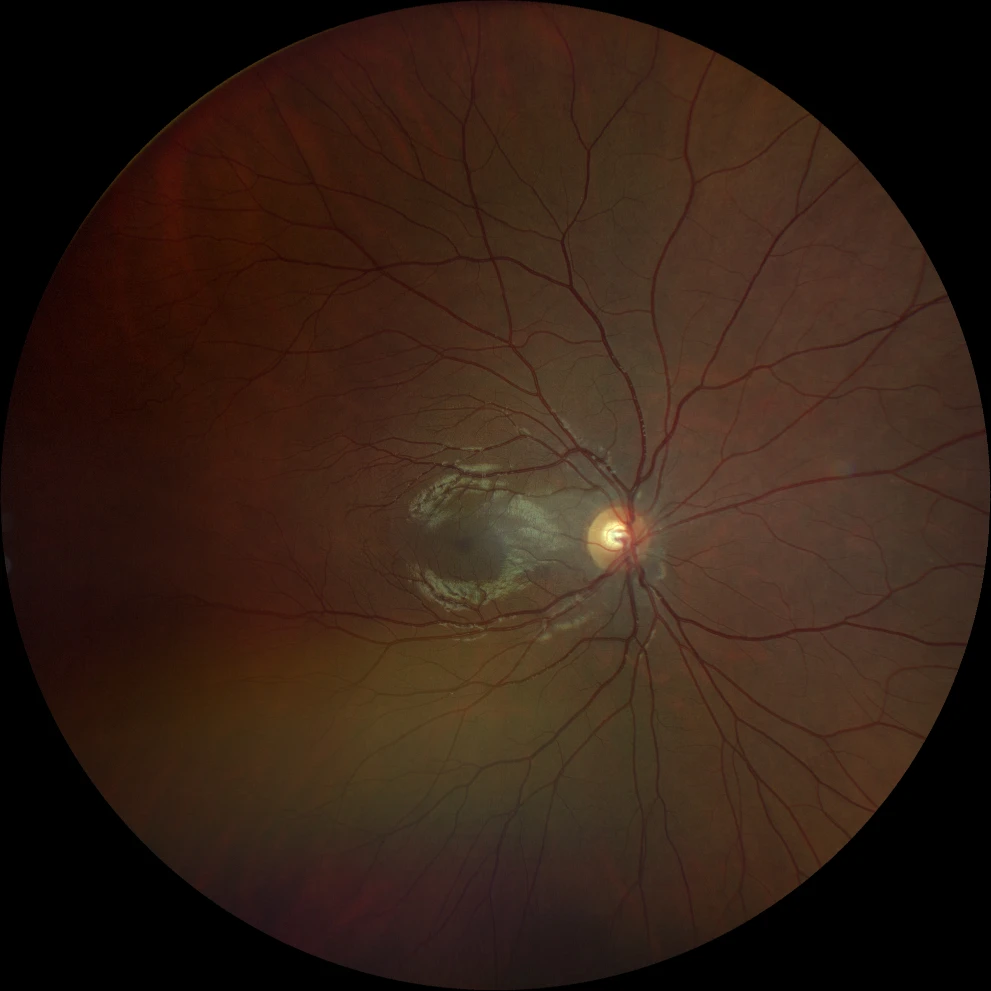
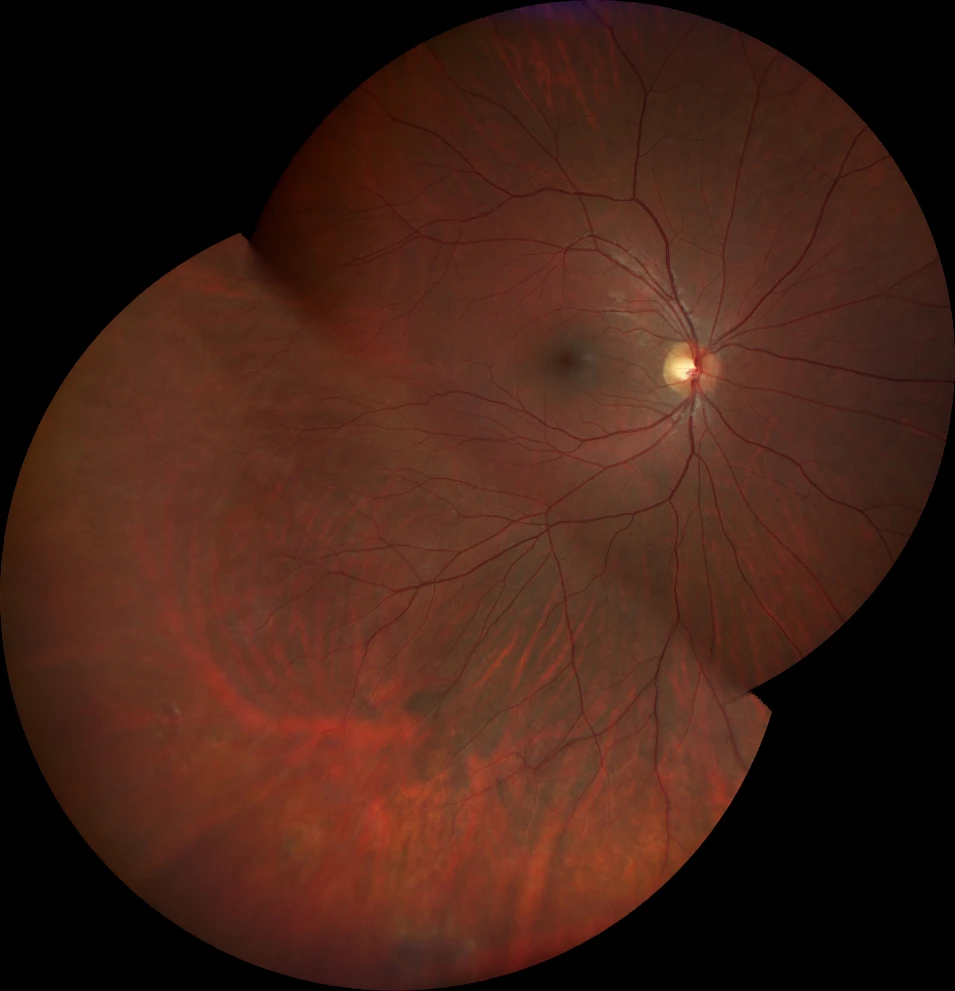
A. Color fundusography (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the older sister's right eye, showing an avascular temporal retina.
B. Color fundus photograph (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the older sister's left eye, showing peripheral panphotocoagulation scars, fibrosing remnants of retinal neovascularization on the temporal side, and remnants of the attached posterior hyaloid (postvitrectomy changes).
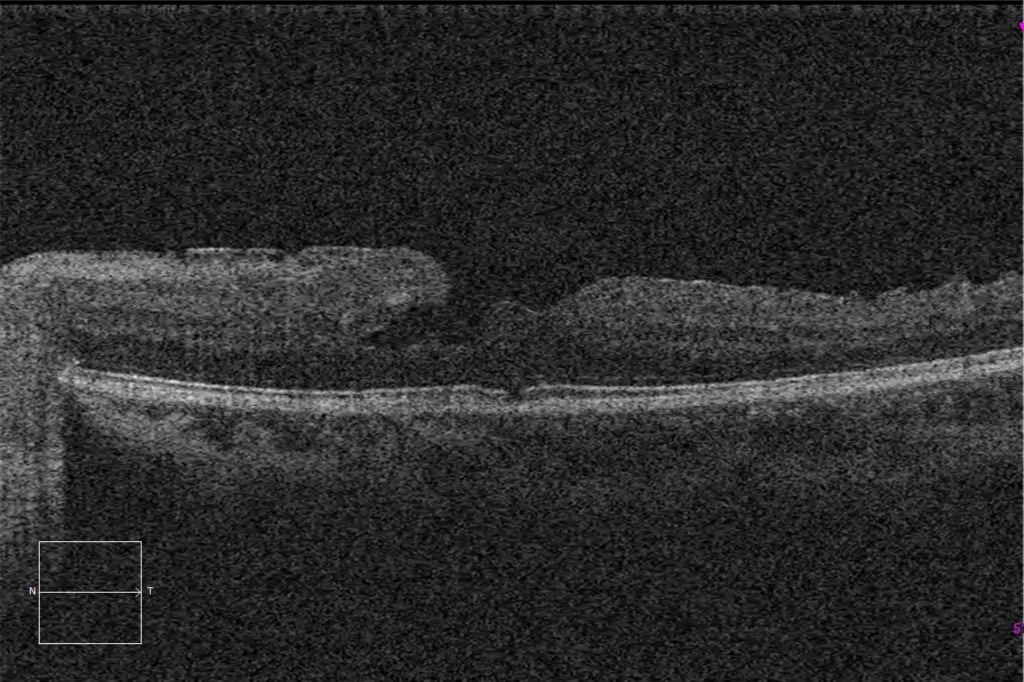
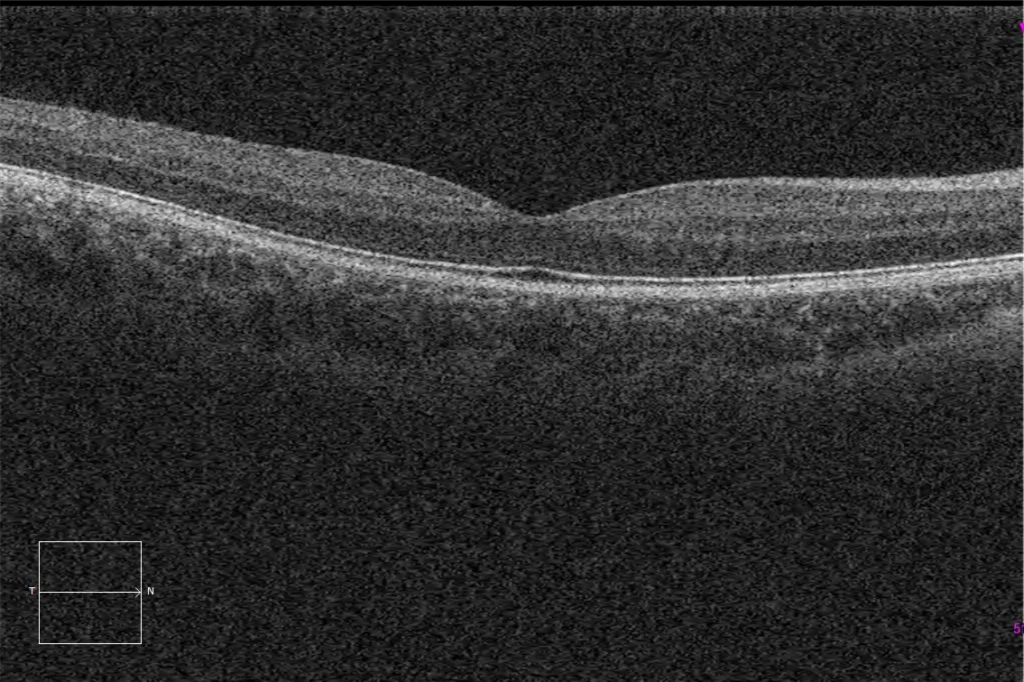
C. Macular HD optical coherence tomography (Cirrus 5000, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the older sister's left eye, showing a lamellar macular hole with a small epiretinal membrane on the nasal side of the hole.
D. Macular HD optical coherence tomography (Cirrus 5000, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the older sister's left eye, showing a mild traction remnant of neovascular tissue on the temporal side of the macula.
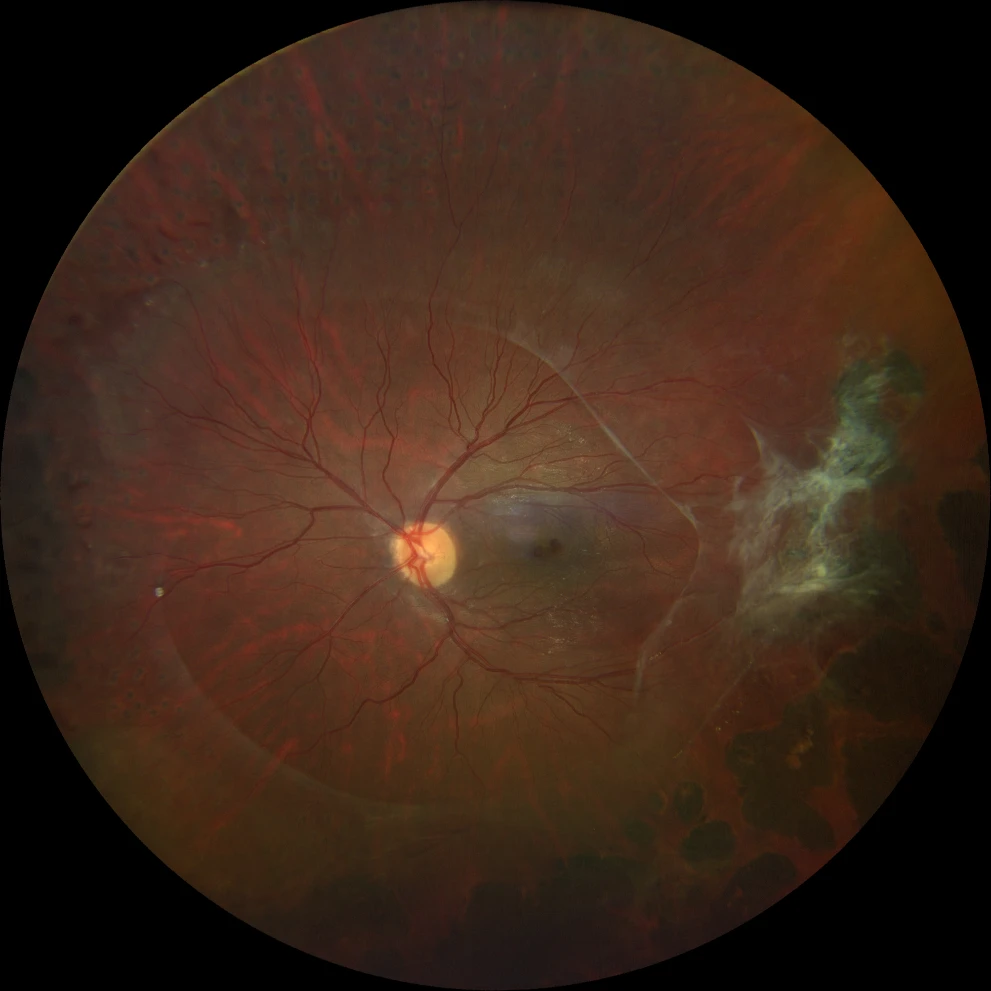
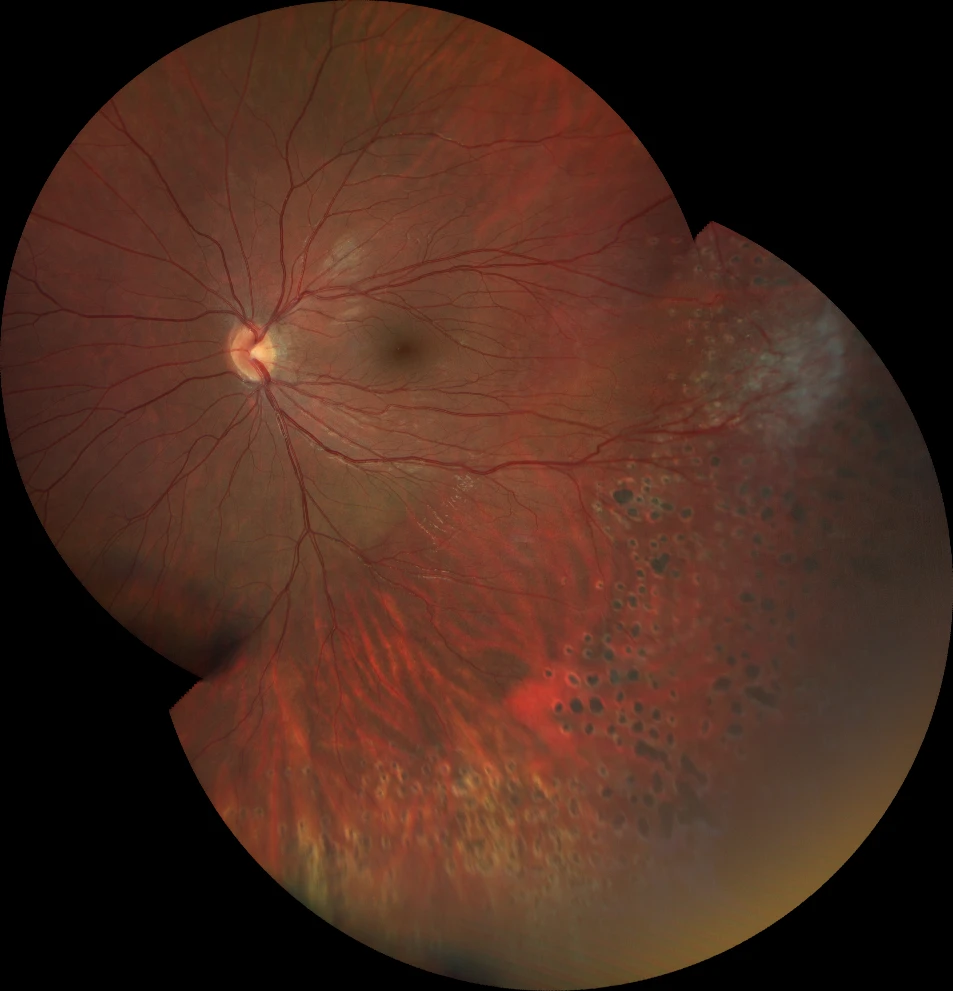
E. Color fundusography (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the younger brother's right eye, showing an avascular temporal retina.
F. Color fundusography (Clarus 500, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the younger brother's left eye, showing peripheral panphotocoagulation scars, fibrosing remnants of retinal neovascularization on the temporal side, and temporal macular traction (macular dragging).
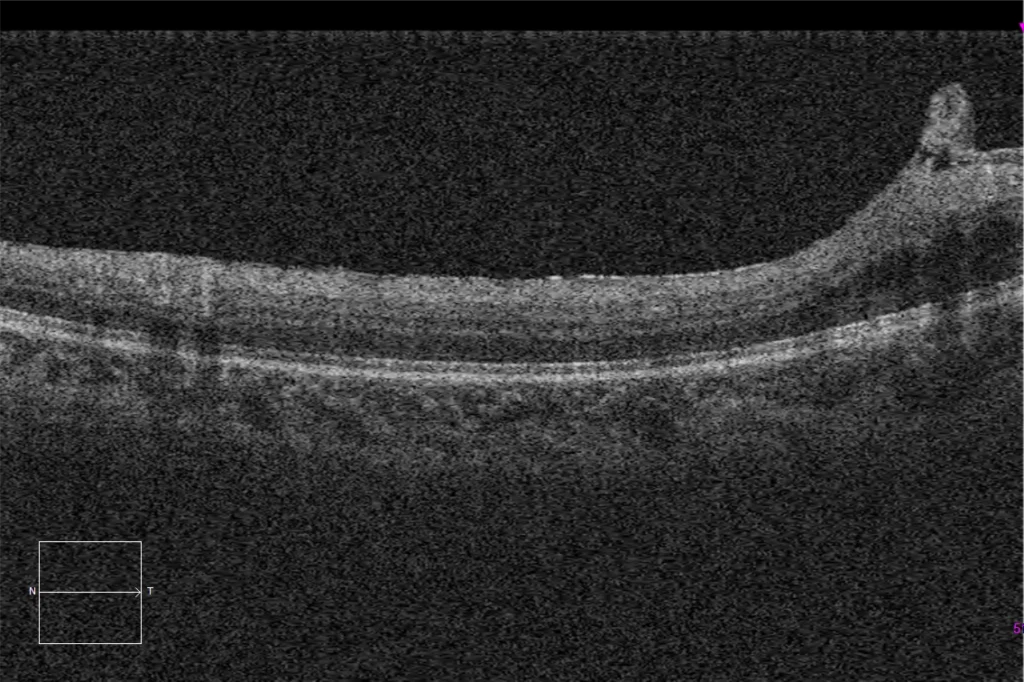
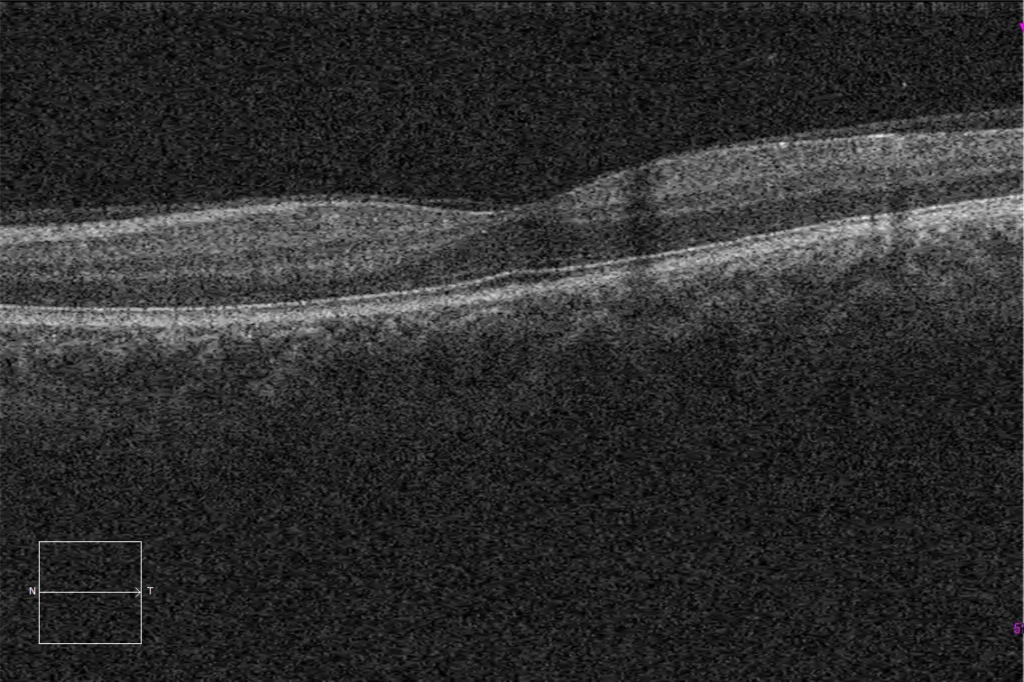
G and H. Macular HD optical coherence tomography (Cirrus 5000, Carl Zeiss Meditec ASG, Jena, Germany) of the younger brother's right and left eyes, showing normal macular structure.
Description
Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy (FEVR) is a group of inherited retinal disorders characterized by abnormal retinal angiogenesis, leading to incomplete vascularization and ischemia in the peripheral retina. Hypoxia in avascular areas can trigger vitreous neovascularization, resulting in vitreoretinal traction, folds, subretinal exudates, vascular displacement, and ultimately, tractional or exudative retinal detachment, derived from increased vascular permeability.
Penetrance is variable and its manifestation is asymmetric, even within the same family, with mixtures of severe and asymptomatic cases. This disorder exhibits genetic heterogeneity, with more than 10 associated genes. Although autosomal recessive and X-linked recessive inheritances (NDP) exist, most cases show autosomal dominant inheritance.