Laminar hole
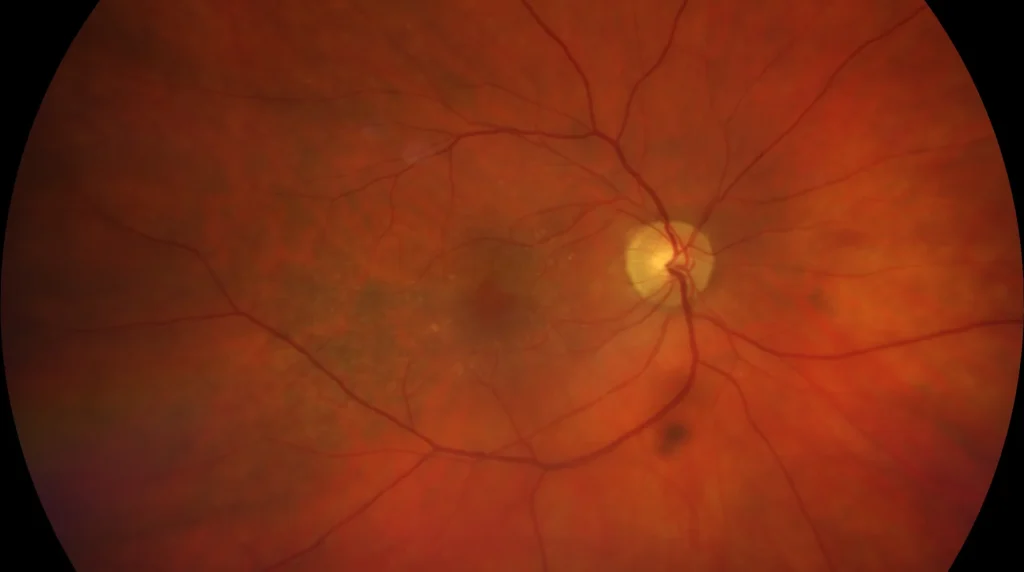
Color retinography (right eye (left), left eye (right)): In both eyes, alterations can be seen at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium in the macular area and a thickness defect can be seen at the foveal level.
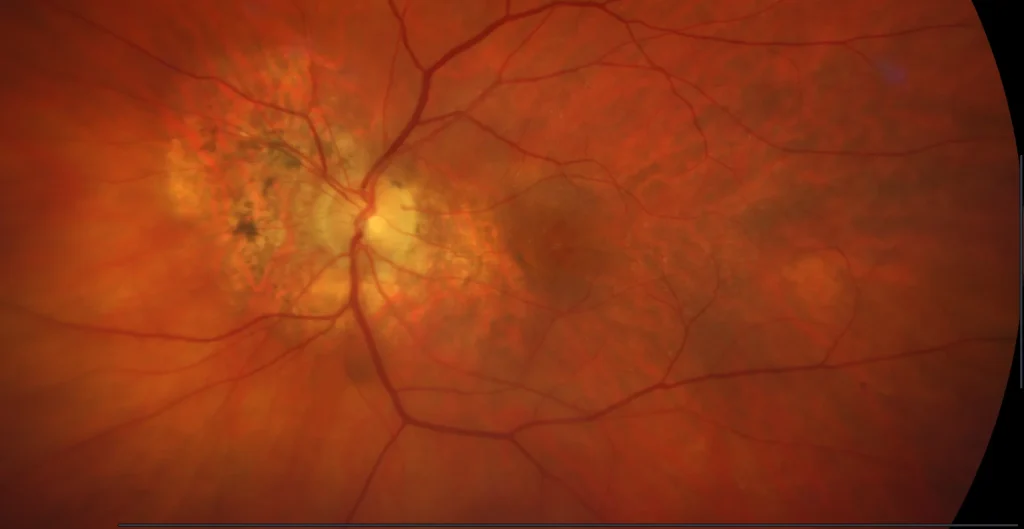
Color retinography (right eye (left), left eye (right)): In both eyes, alterations can be seen at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium in the macular area and a thickness defect can be seen at the foveal level.
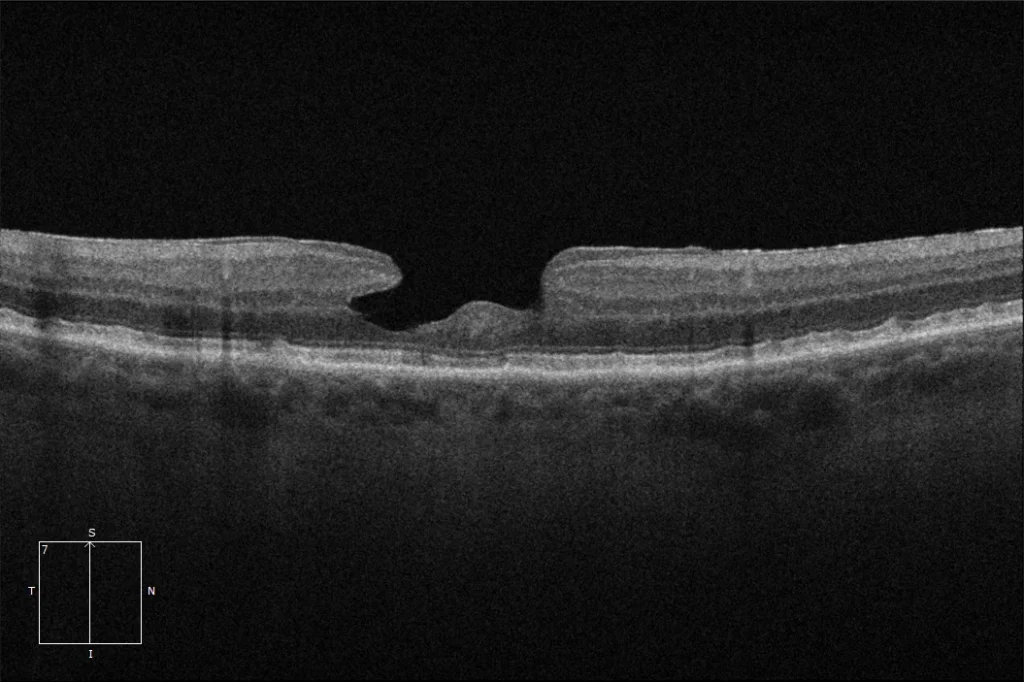
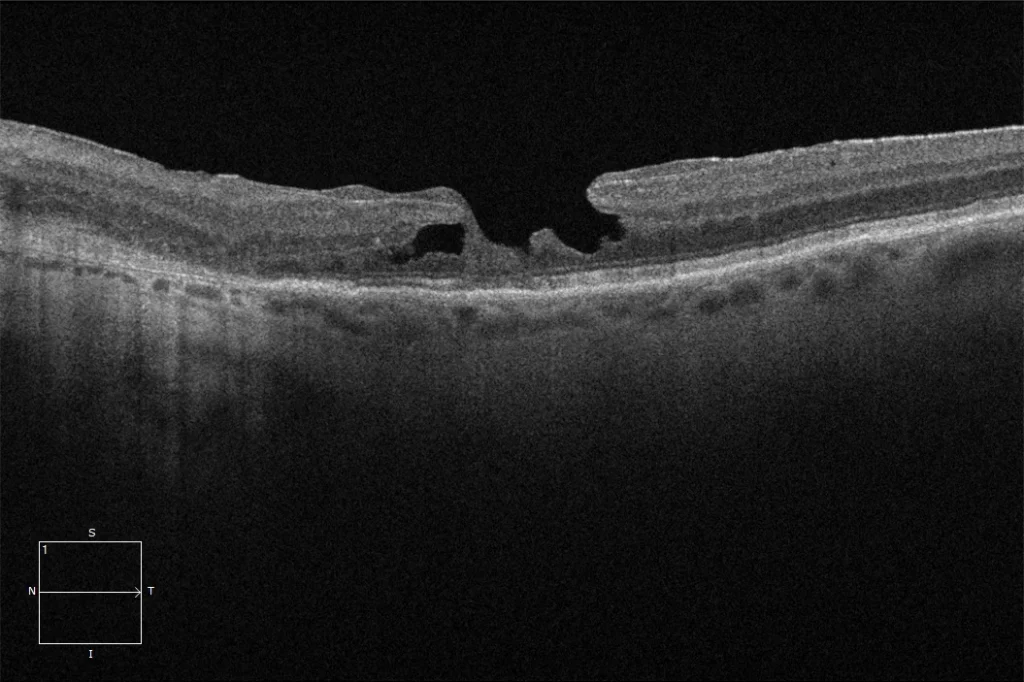
Macular OCT: Bilateral laminar hole in which a defect in the thickness of the inner layers of the retina at the foveal level can be seen. The outer layers of the retina are preserved.
Description
Lamellar macular hole is a vitreoretinal disorder characterized by an irregular foveal contour and a break in the inner layers of the fovea. This pathology involves a separation of the inner retina from the outer retina, without a full-thickness defect in the fovea, with intact photoreceptors in this area. Bilateral appearance of this condition is rare, with an estimated prevalence in the literature of between 5% and 30%.