Pachychoroid Neovasculopathy
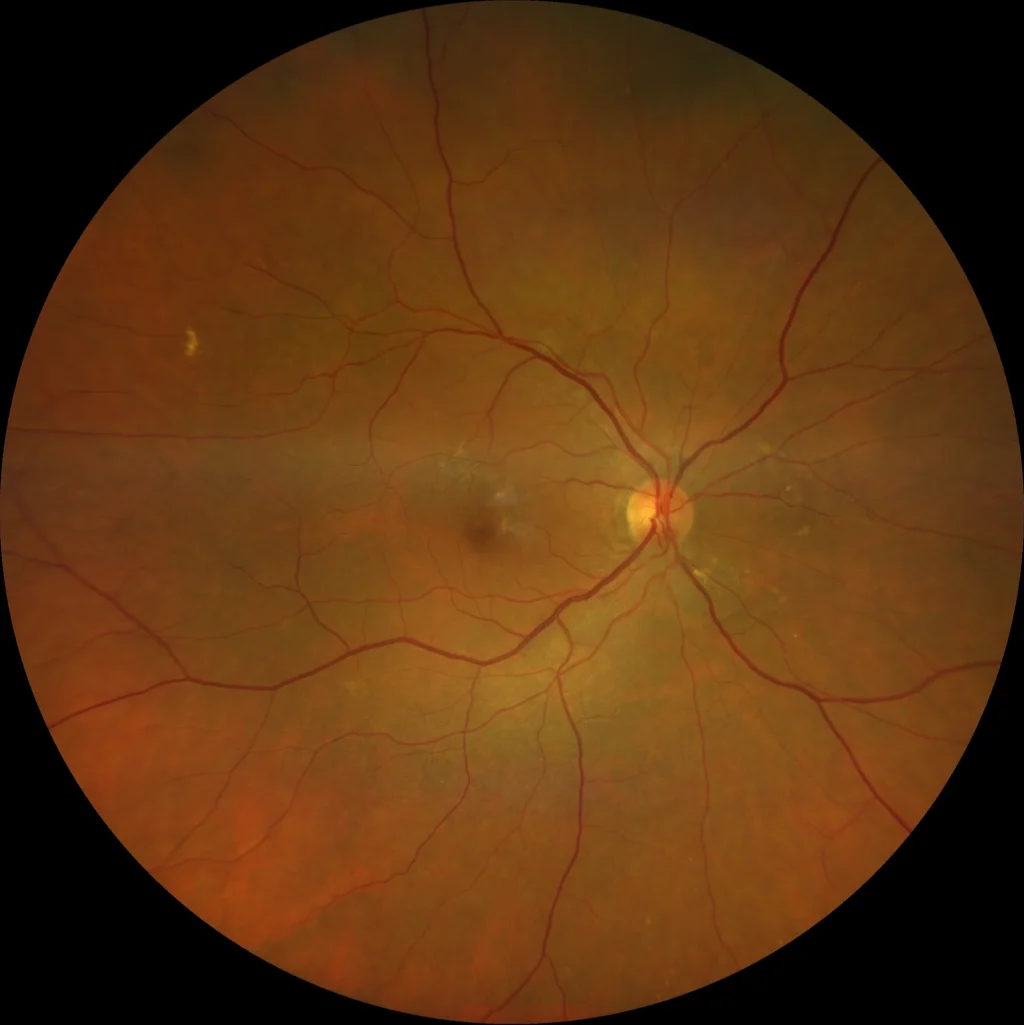
Color fundus (Clarus500, Zeiss): (A): OD Perifoveal and peripapillary pigmentary changes. No hemorrhages, drusen or other signs of AMD are seen.
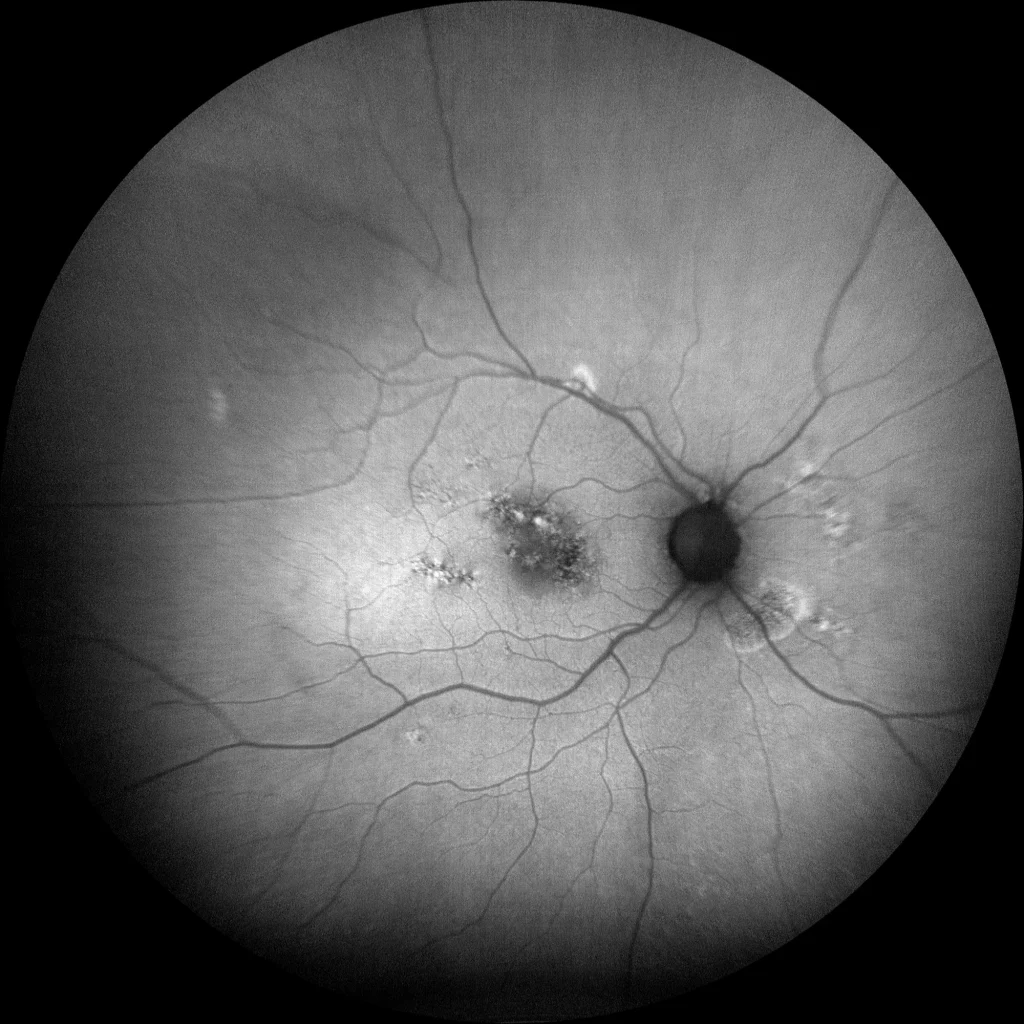
Autofluorescence (Clarus500, Zeiss): (B) OD: Autofluorescence reveals alterations in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) located in the macular and peripapillary area in the form of hypo- and hyperautofluorescent granular lesions.
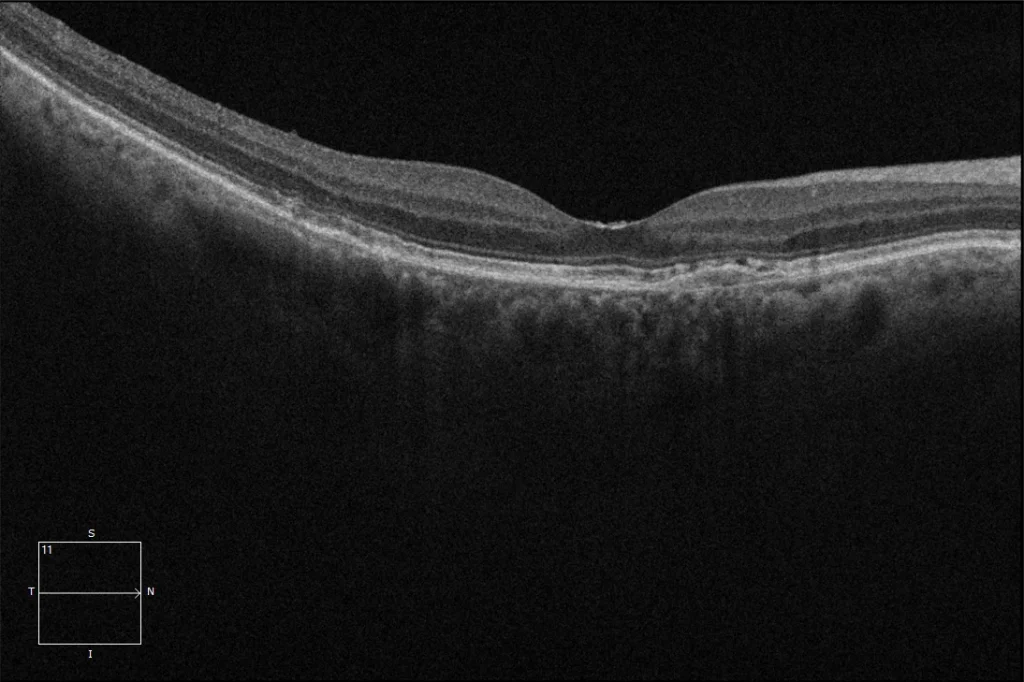
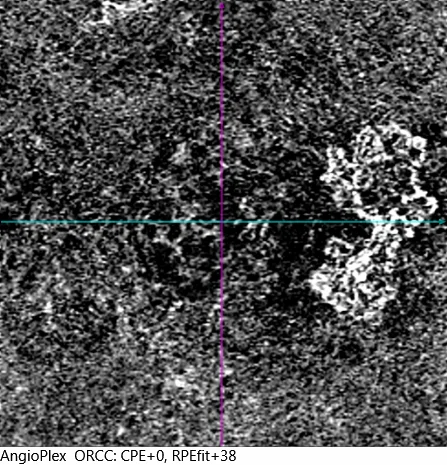
(C) OD macular OCT: Flat RPE detachment (PED), known as SIRE (shallow irregular RPE elevation), defined as an elevation or detachment of the RPE with a height no greater than 100 microns and a diameter greater than 1000 microns. The choroid presents pachychoroid characteristics with increased thickness due to pachyvessels in the Haller's layer.
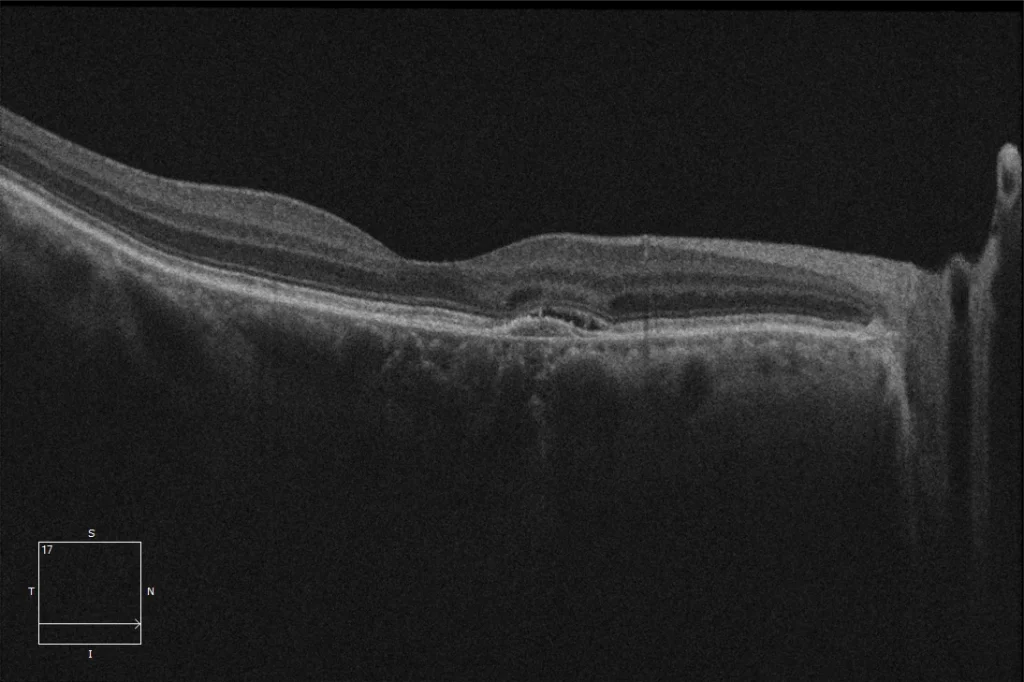
(D) OD macular OCT 2. In this section, a possible minimal subretinal fluid is observed that appears and disappears without treatment and is not considered an indicator of activity in this case.
Description
Pachychoroid neovasculopathy. The spectrum of pachychoroid diseases refers to a group of conditions that share the pachychoroid phenotype, represented by a series of choroidal morphological alterations characterized by:
- Focal or diffuse choroidal thickening (increased thickness of Haller’s layer)
- Pachyvessels in Haller’s layer.
- Attenuation of the inner choroid: Thinning of the choriocapillaris and Sattler’s layer.
- Choroidal vascular hyperpermeability in indocyanine green angiography
- Choroidal ischemia
Pachychoroid neovasculopathy is one of the pathologies included within pachychoroid diseases and is defined as the presence of type 1 neovascularization (below the RPE) with pachychoroid characteristics and without evident signs of central serous chorioretinopathy or AMD. These neovascularizations often have a low degree of activity without producing fluid or exudation and without causing symptoms in the patient. In these cases, treatment with antiangiogenics is controversial.
It can sometimes be difficult to differentiate a pachychoroid neovasculopathy from a central erosic chorioretinopathy (CSC) with an associated neovascular membrane and we have to be guided by the patient’s clinical history and the absence of CSC episodes.