Racemose Hemangioma
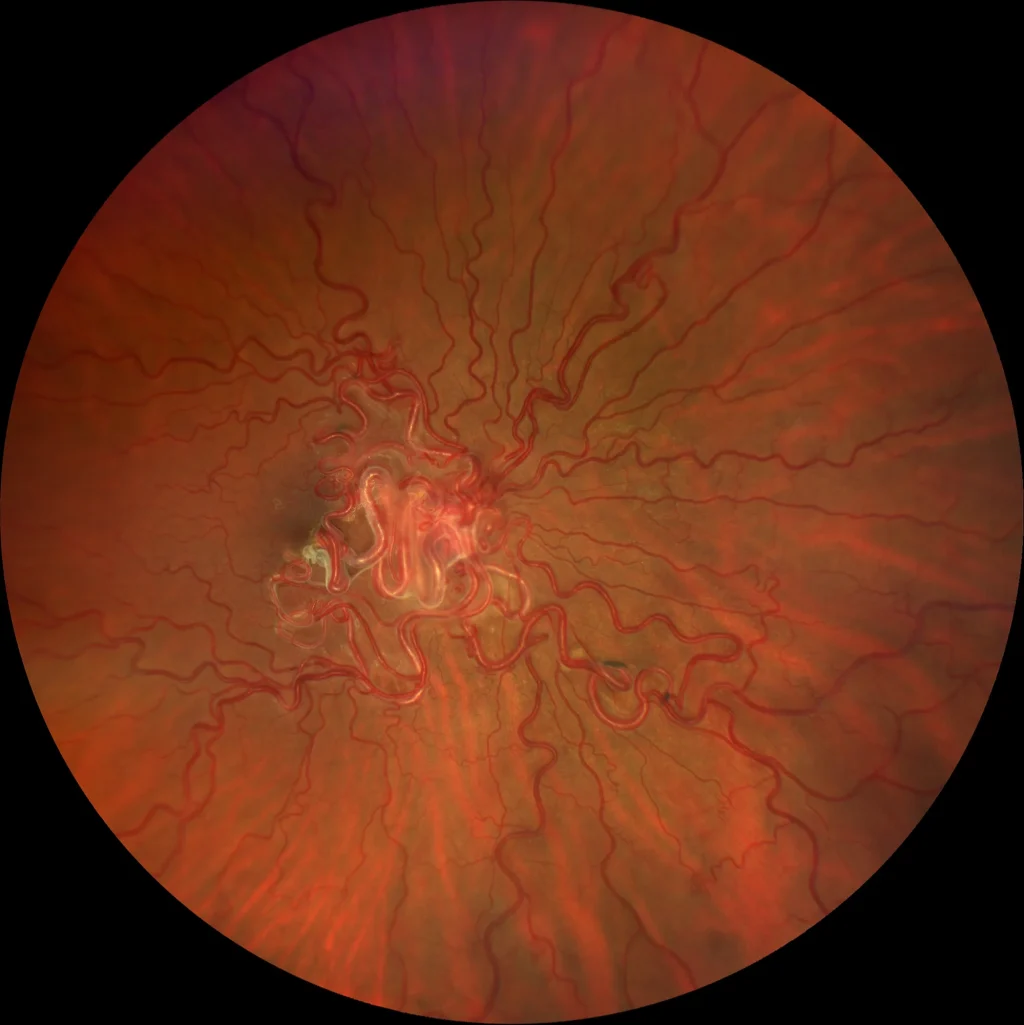
Color retinography OD: Group 3 racemose hemangioma. Large dilated retinal vessels can be seen entering and leaving the papilla, as well as direct arteriovenous communications.
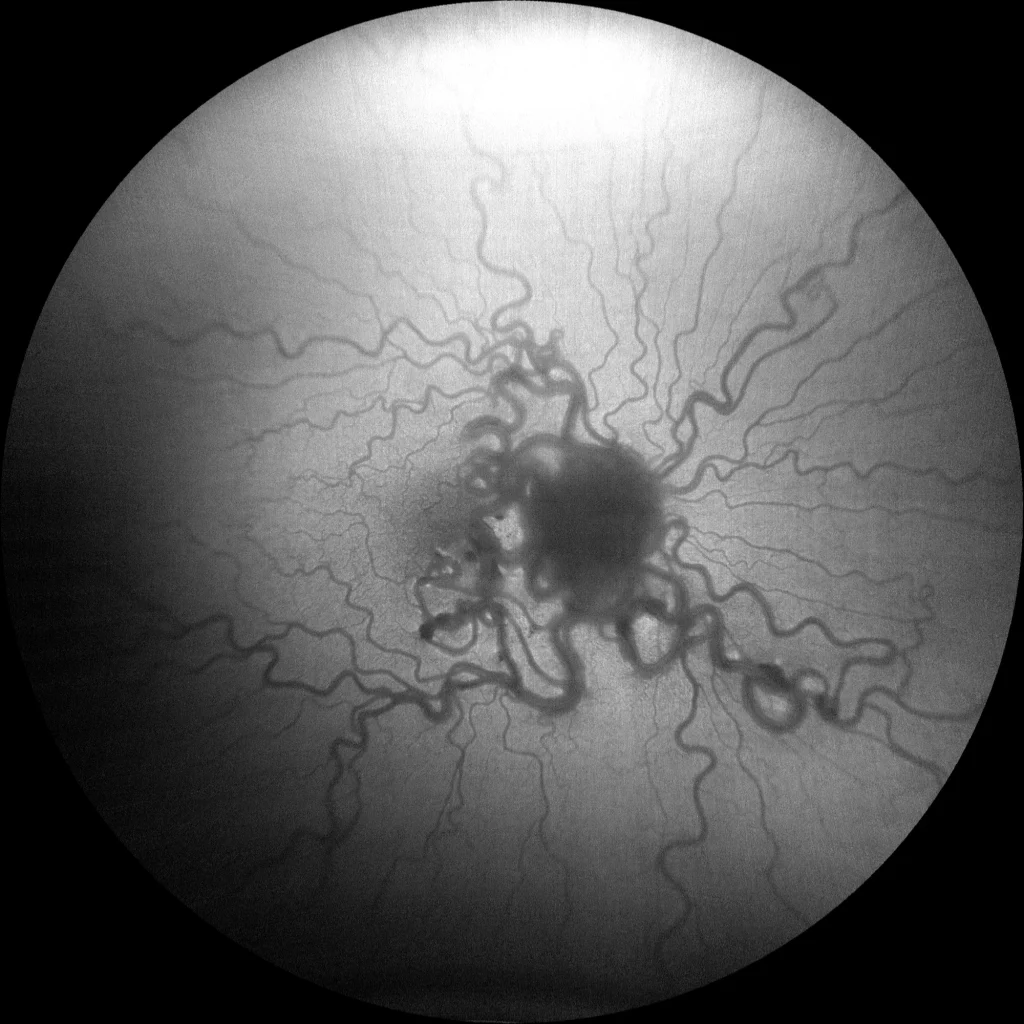
OD autofluorescence: In autofluorescence, the large vessels that form part of the hemangioma are seen to be hypoautofluorescent.
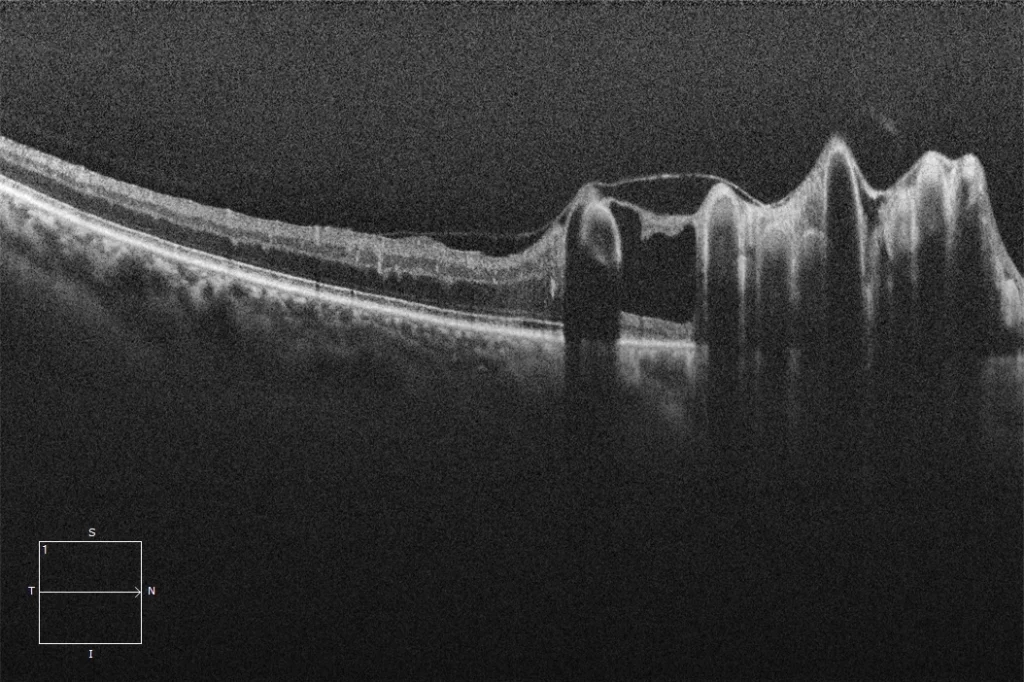
Macular OCT OD: Different slices of the macular OCT show large hyperreflective intraretinal vessels with posterior shadow that are part of the hemangioma and that protrude the inner retina towards the vitreous cavity, generating some areas of hyporeflective retinoschisis.
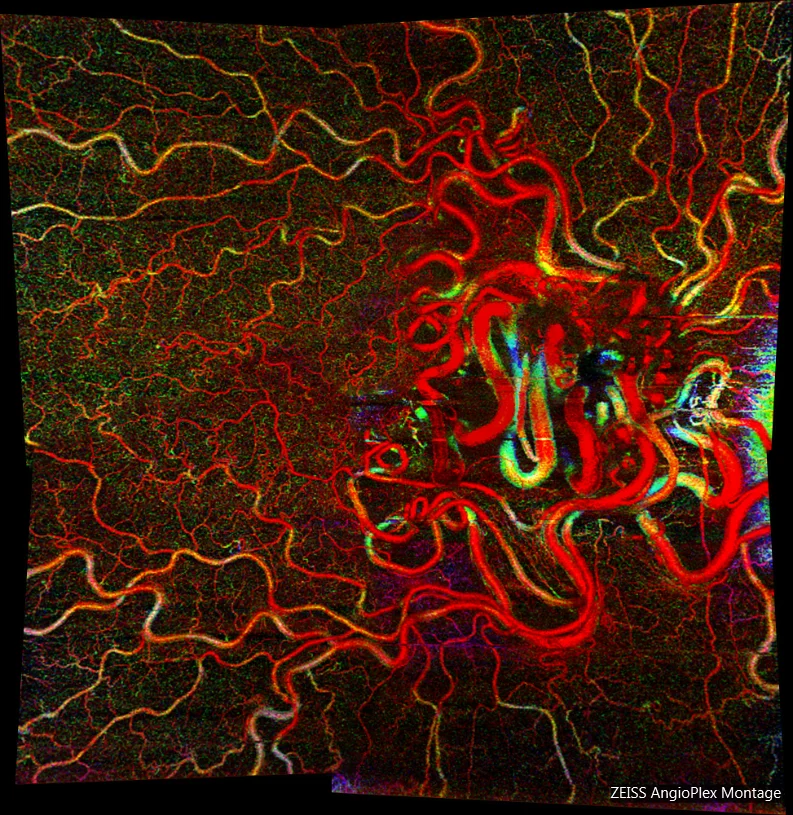
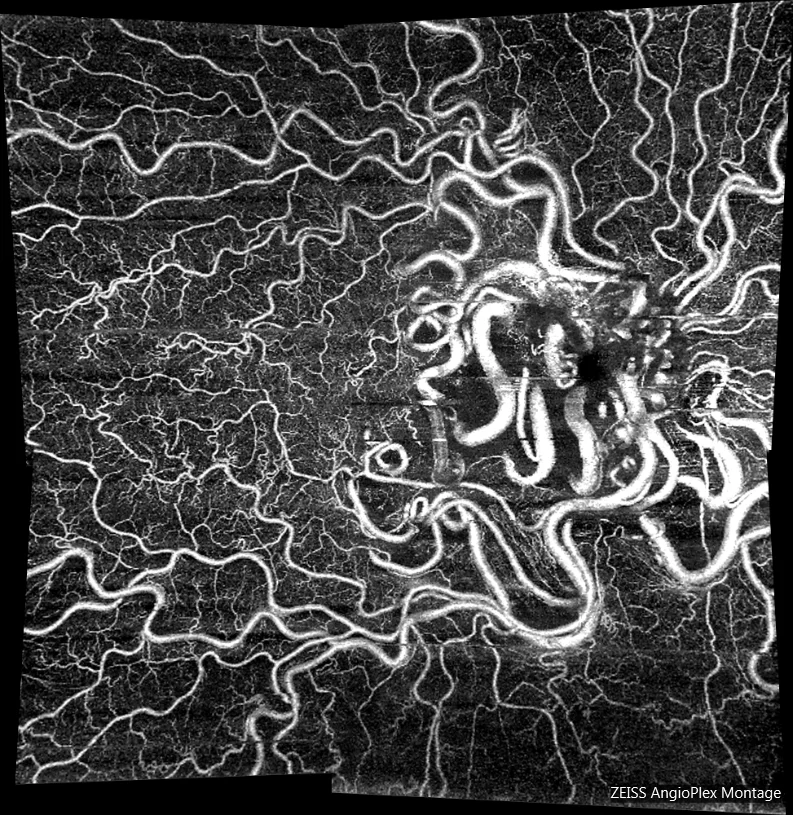
Angio OCT OD: In the montage made by the angio-OCT, the entire vascular structure of the hemangioma can be seen.
Description
Racemose hemangioma, also called retinal arteriovenous malformation, is a hemangioma of the retina or optic nerve that may be part of Wyburn-Mason syndrome, a rare condition characterized by the formation of central nervous system hemangiomas and ipsilateral retinal hemangiomas. Lesions are typically unilateral, nonhereditary (spontaneous) and located in the retina or optic nerve. Retinal hemangiomas are divided into 3 groups (Archer classification):
- Group 1: Interposition of an anomalous capillary plexus between the main vessels that form the arteriovenous communication. It is asymptomatic. Intracranial involvement is rare.
- Group 2: Direct arteriovenous communication without capillary plexus interposition. Mild visual symptoms. May be associated with intracranial malformations.
- Group 3: Extensive and complex arteriovenous communication. Dilated arteries emerging from the optic nerve form arteriovenous communications in the retina and return to the optic nerve as dilated veins. Visual loss. High risk of intracranial malformations.