Retinal capillary hemangioma
Description
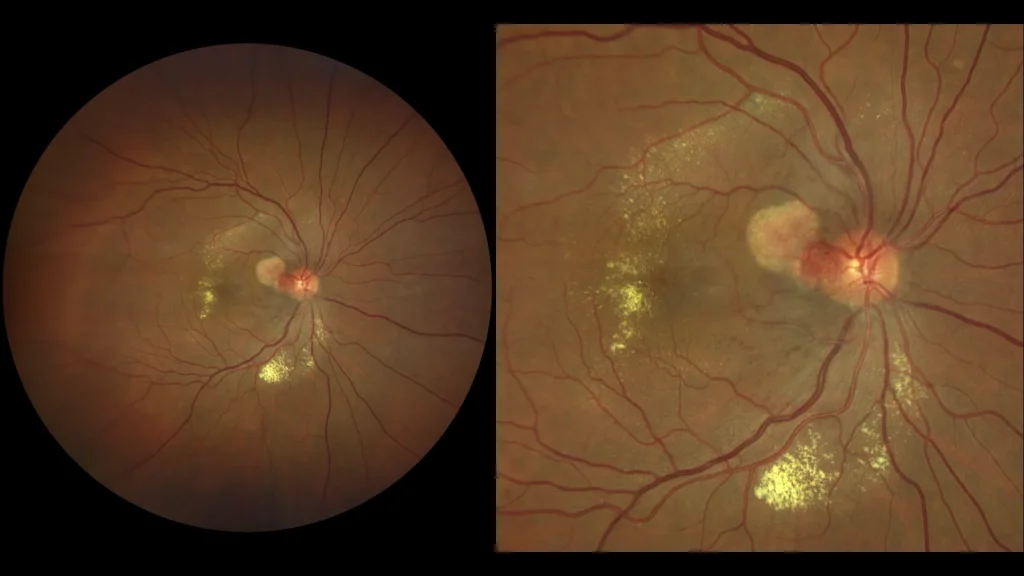
Retinal capillary hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor that develops in the retina and is frequently associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL), an autosomal dominant genetic condition. These hemangiomas may be solitary or multiple and present as reddish or orange nodules in the retina, often with dilated and tortuous feeder vessels.
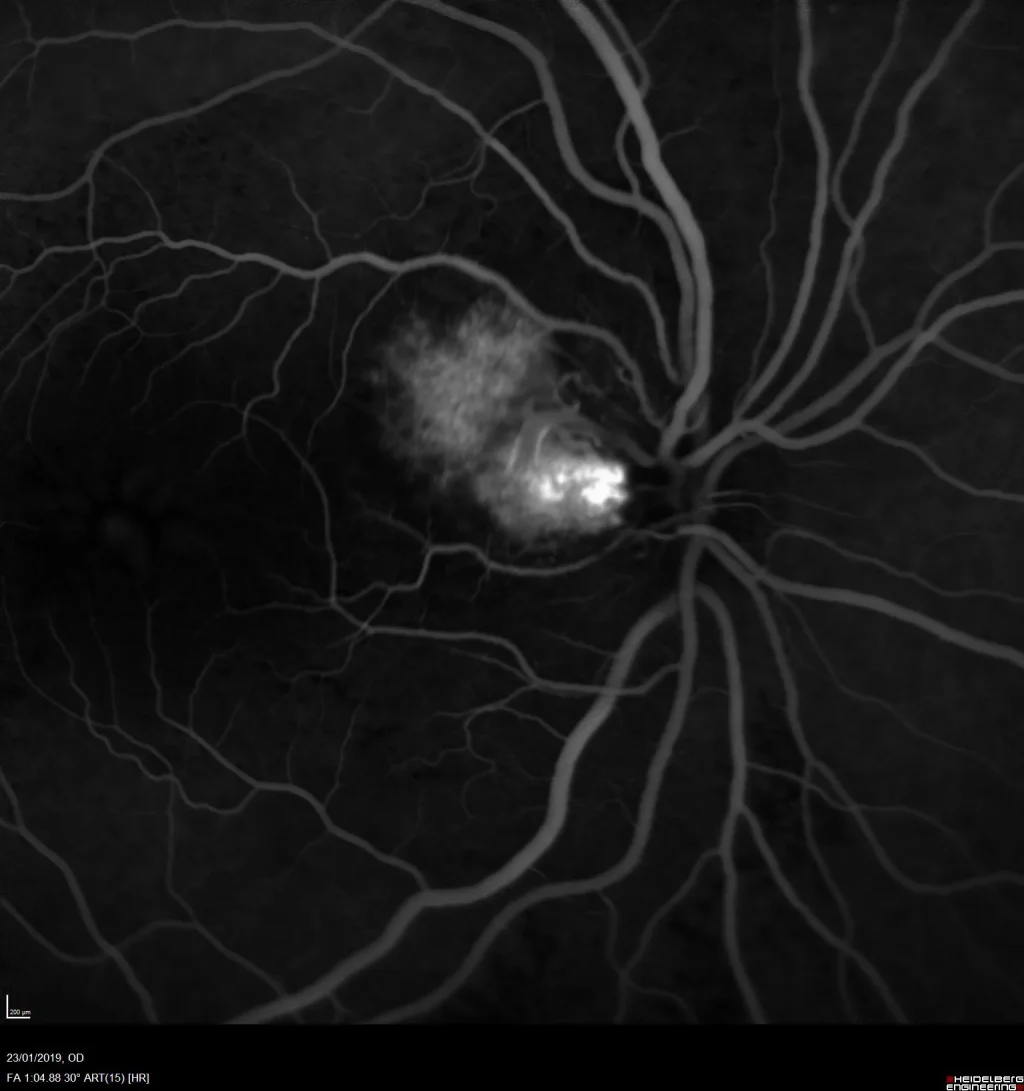
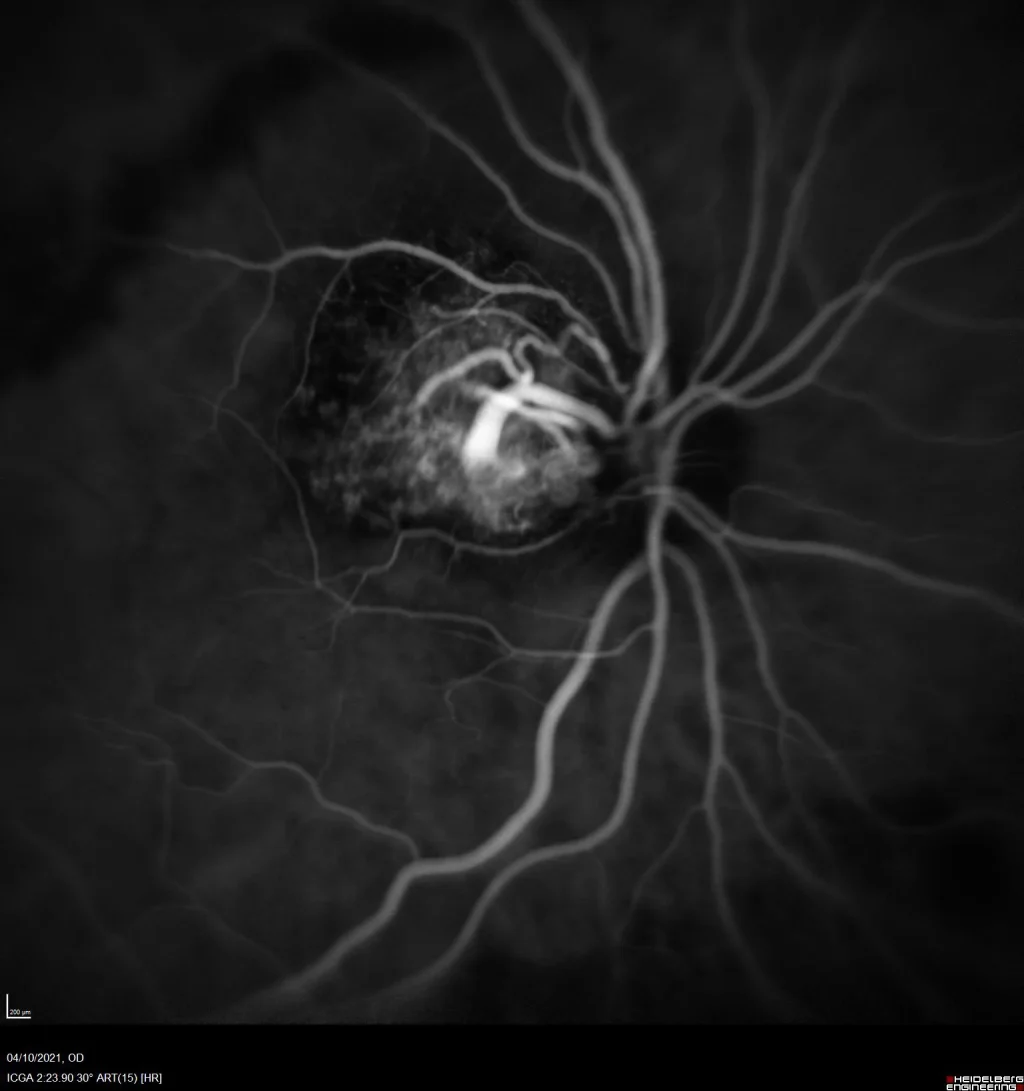
Clinically, patients may experience blurred vision, vision loss, and sometimes visual distortion due to associated exudates or hemorrhages. Diagnosis is made by ophthalmoscopy, where characteristic vascular lesions are observed, and confirmed by fluorescein angiography, which shows the filling pattern and drainage of the tumor.
Treatment for retinal capillary hemangioma depends on the size and location of the tumor. Options include laser photocoagulation, cryotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and in some cases intravitreal injections of antiangiogenic agents. Regular monitoring is crucial, especially in patients with VHL, because of the risk of developing other tumors in the eye and elsewhere in the body.
Early intervention is essential to prevent complications such as retinal detachment, macular edema and irreversible vision loss. The management of these patients is usually multidisciplinary, involving ophthalmologists, geneticists and other specialists for a comprehensive approach to the disease.