< back
RPE hamartomas associated with family adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
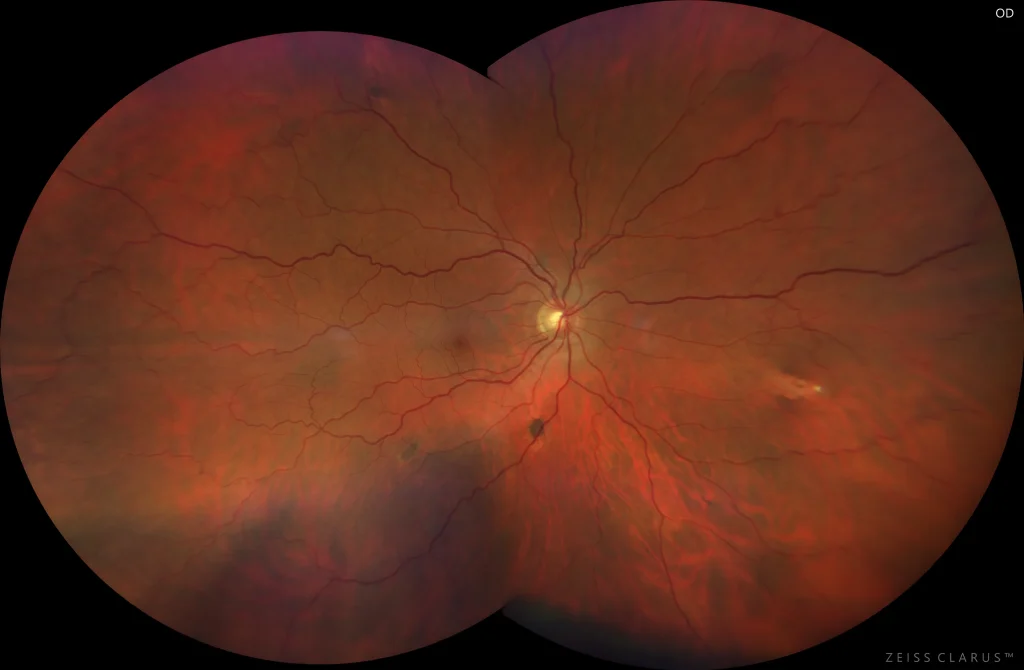
UWF color retinography (Clarus 700, Zeiss): Multiple bilateral irregular pigmented lesions of various shapes and sizes.
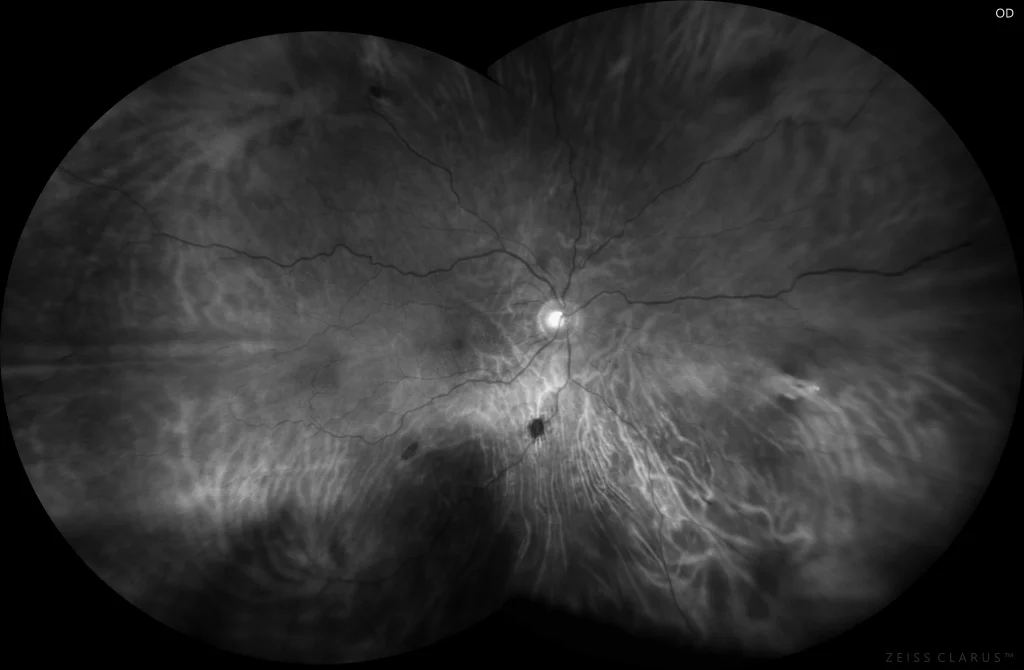
Red filter retinography (Clarus 700, Zeiss): Pigmented lesions are more easily visible when using the red filter.
Description
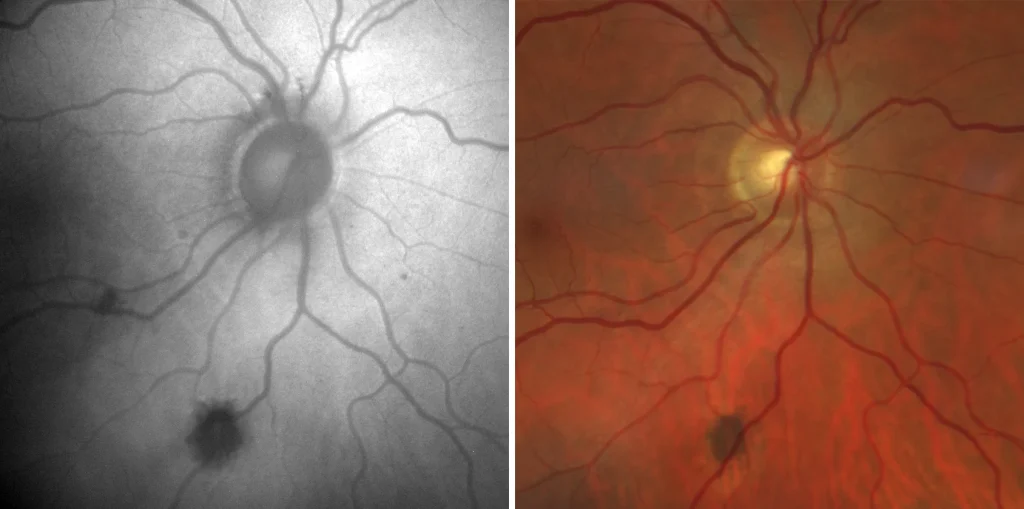
Pigmented fundus lesions associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) are multiple bilateral lesions, with poorly defined borders, sometimes depigmented, and a random, non-sectoral distribution. These lesions must be differentiated from solitary and grouped HCEPR in bear tracks. FAP is an autosomal dominant disorder that is associated with colon cancer in almost 100% of patients.