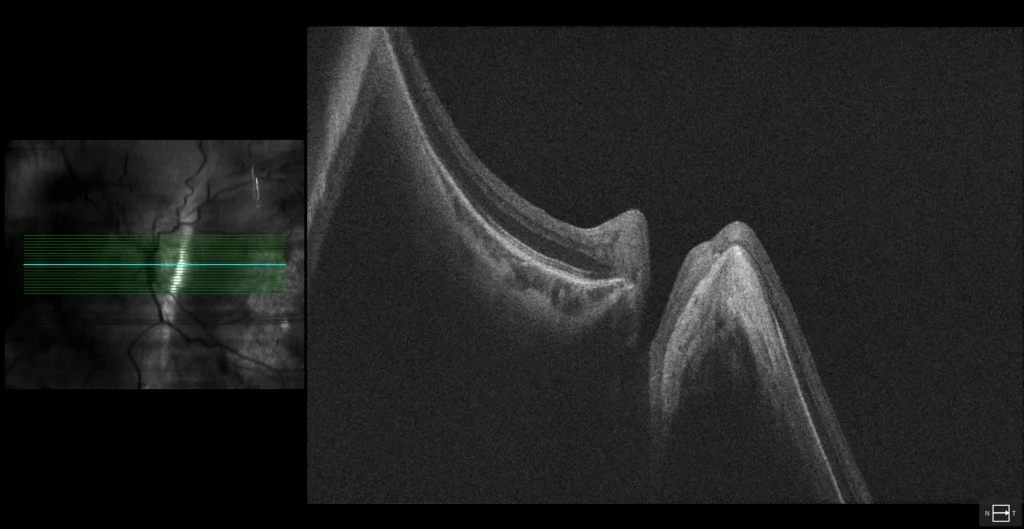
Septated staphyloma with myopic macular neovascularization
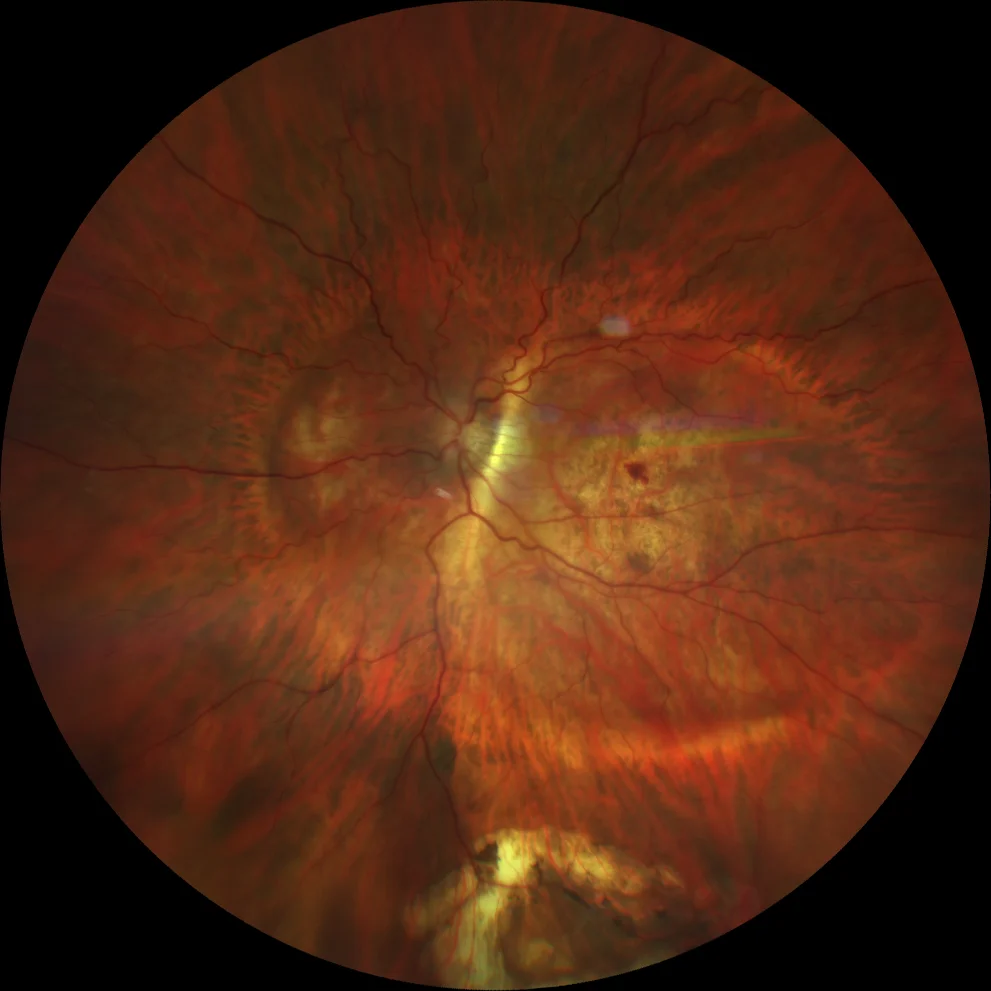
(Clarus 700, Zeiss): posterior staphyloma encompassing the macula and optic disc with an intermediate septum between the fovea and the optic disc (Curtin type IX staphyloma). Central macular hemorrhage
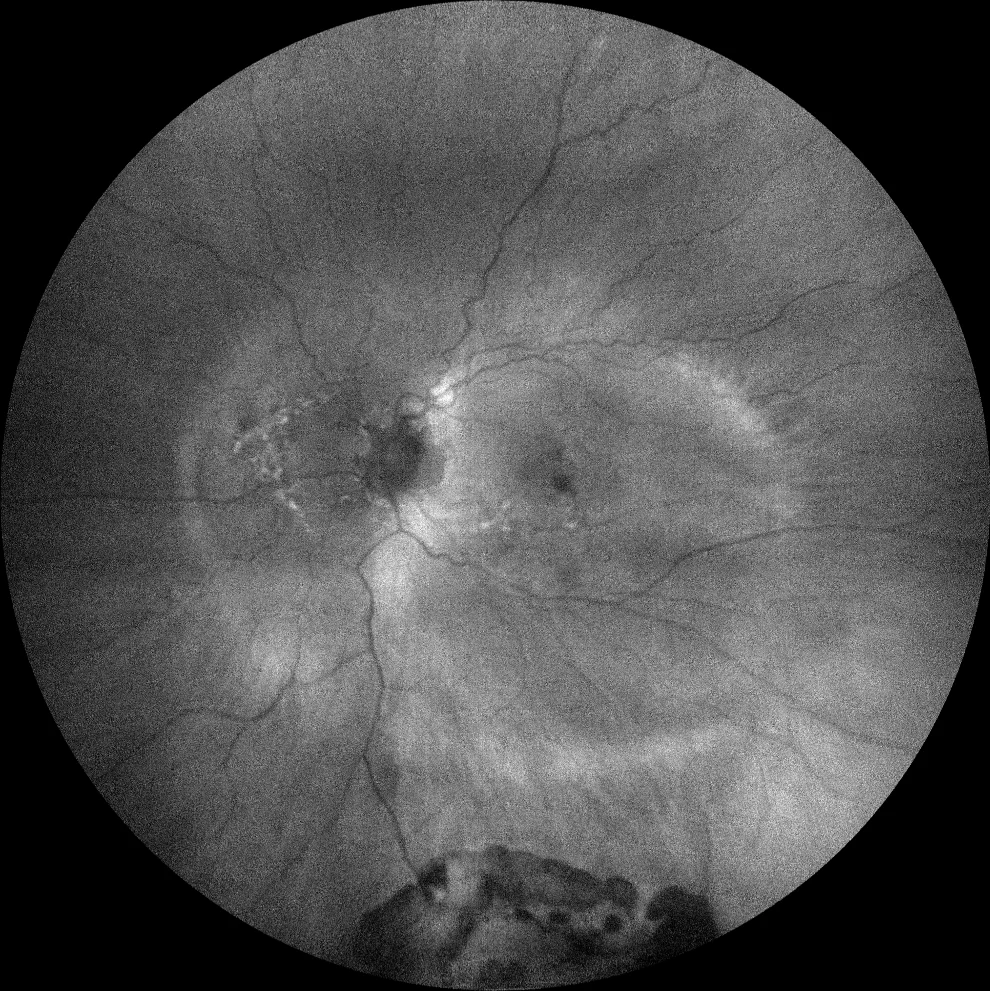
Green autofluorescence (Clarus 700, Zeiss): a hyperautofluorescent line is observed that allows clear delineation of the staphyloma, as well as visualization of the septum
Description
A 66-year-old male presents with a 2-week history of central scotoma in the left eye. His ophthalmic history includes pathological myopia in both eyes, LASIK in both eyes (21 years ago), retinal detachment (RD) in the left eye (treated with vitrectomy 8 years ago), and cataract surgery in the left eye (performed 8 years ago).
VA OD 20/20 OS 20/50.
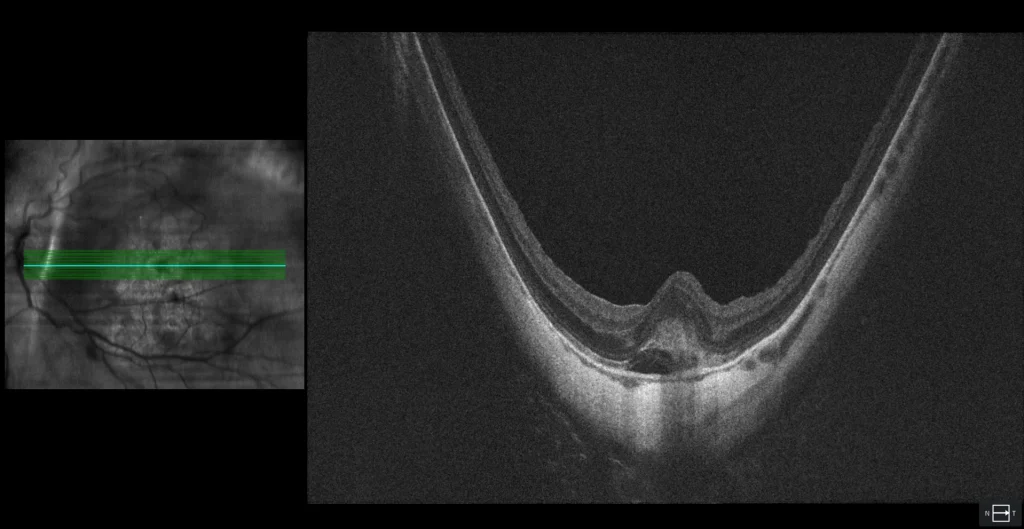
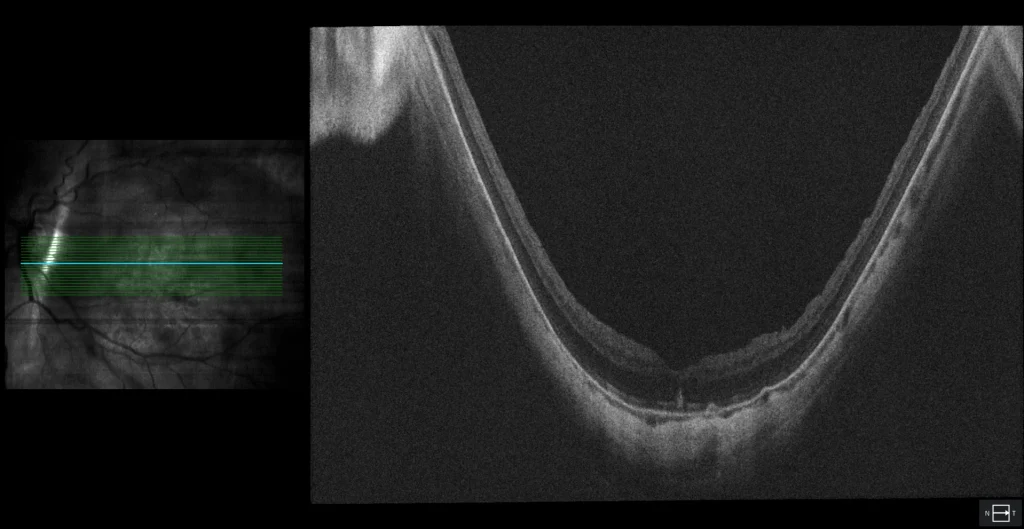
The fundus examination of the left eye shows a staphyloma encompassing the macula and optic disc with a septum between the fovea and the optic disc (Curtin type IX staphyloma). Additionally, a central macular hemorrhage is visible in the context of diffuse chorioretinal atrophy. A peripheral pigmented scar is also observed at 6 o’clock, corresponding to the tear associated with the RD that was surgically treated 8 years ago. Green autofluorescence clearly shows the boundaries of the posterior staphyloma. OCT reveals hyperreflective subretinal material (SHRM) without a hyporeflective space between this material and the RPE, and a small amount of subretinal fluid (SRF), suggesting the presence of myopic macular neovascularization (CNV). After 3 anti-angiogenic injections, the SHRM was almost completely reabsorbed, and vision improved to 20/25.